Kubernetes NGINX Ingress

- How to Use Nginx Ingress Controller
- Testing the Ingress
- Adding a Node.js / Express.js Web App
- Adding TLS
An Ingress is an application that allows you to access your Kubernetes services from outside the Kubernetes cluster. This lets you consolidate your routing rules into a single resource, e.g.:
- mydomain.com/api/web/ leads to an api service for your web application
- mydomain.com/api/mobile/ leads to an api-v2 service for the mobile access
The Ingress enables you make your services available without having to use LoadBalancers (only available on Cloud solutions like AWS, GCE, Azure...) or exposing each service on the Node (NodePort). Making this the ideal solution for an on-premise hosting of an Kubernetes Cluster.
Popular Ingress Controllers include:
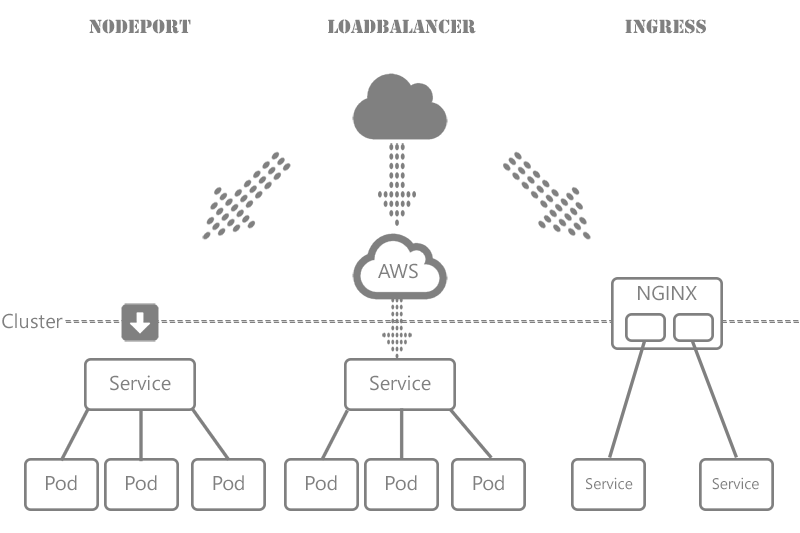
How to Use Nginx Ingress Controller
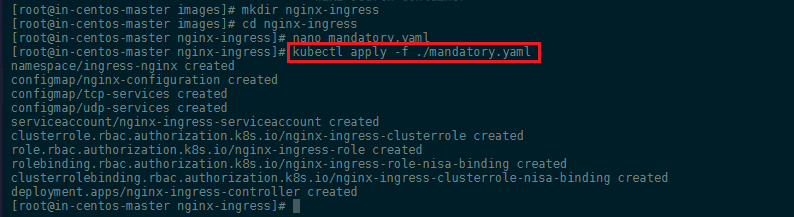
Creating the resources for Nginx Ingress
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/master/deploy/mandatory.yaml
Or create the mandatory.yaml file locally and create the prerequisites with kubectl apply -f mandatory.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
---
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: nginx-configuration
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
---
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: tcp-services
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
---
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: udp-services
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-serviceaccount
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-clusterrole
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
- endpoints
- nodes
- pods
- secrets
verbs:
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- services
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- "extensions"
resources:
- ingresses
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- events
verbs:
- create
- patch
- apiGroups:
- "extensions"
resources:
- ingresses/status
verbs:
- update
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-role
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
- pods
- secrets
- namespaces
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
resourceNames:
# Defaults to "<election-id>-<ingress-class>"
# Here: "<ingress-controller-leader>-<nginx>"
# This has to be adapted if you change either parameter
# when launching the nginx-ingress-controller.
- "ingress-controller-leader-nginx"
verbs:
- get
- update
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
verbs:
- create
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- endpoints
verbs:
- get
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-role-nisa-binding
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: nginx-ingress-role
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nginx-ingress-serviceaccount
namespace: ingress-nginx
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-clusterrole-nisa-binding
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: nginx-ingress-clusterrole
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nginx-ingress-serviceaccount
namespace: ingress-nginx
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-controller
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
annotations:
prometheus.io/port: "10254"
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
spec:
serviceAccountName: nginx-ingress-serviceaccount
containers:
- name: nginx-ingress-controller
image: quay.io/kubernetes-ingress-controller/nginx-ingress-controller:0.23.0
args:
- /nginx-ingress-controller
- --configmap=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/nginx-configuration
- --tcp-services-configmap=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/tcp-services
- --udp-services-configmap=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/udp-services
- --publish-service=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/ingress-nginx
- --annotations-prefix=nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: true
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
add:
- NET_BIND_SERVICE
# www-data -> 33
runAsUser: 33
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
- name: https
containerPort: 443
livenessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 10254
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 10
readinessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 10254
scheme: HTTP
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 10
---
Creating the Load Balancing Service
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/master/deploy/provider/baremetal/service-nodeport.yaml
Or again, create the nodeport-ingress-service.yaml file locally and create the Ingress service with kubectl apply -f nodeport-ingress-service.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: ingress-nginx
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
protocol: TCP
- name: https
port: 443
targetPort: 443
protocol: TCP
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
externalIPs:
- <add the IP address of your Kubernetes Master here>
---
I am using the Kubernetes cluster on an on-premise cloud service that does not provide a LoadBalancer. The Bare-Metal solution is something I am working towards, but did implement yet. So this is an old-school DIY cluster and for some reasons the official documentation lead me to a situation where I did not get an IP address on my Ingress service. The solution that I found was to add my external IP (this is the WAN IP of my Kubernetes Master - e.g.
externalIPs: 172.56.4.112- if you install another server in-front of your cluster on the local area network, you should also be able to use the LAN address of your Master here instead - avoiding exposing your cluster directly to the internet) to the service configuration above. Afterwards I was able to access the apps behind this service through this IP address - see below.
This has set up the Nginx Ingress Controller - you can check that it is running with the following command:
kubectl get pods --namespace ingress-nginx
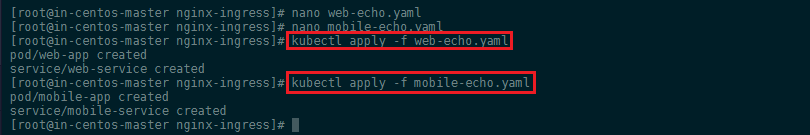
Create two Web Apps to Respond to the incoming Traffic
Now, we can create Ingress resources in our Kubernetes cluster and route external requests to our services. For this we need two services that represent the Ingress routes for our requests. To test this, we can use two web applications that just echo a string, when they receive an HTTP GET command:
web-echo.yaml
kind: Pod
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: web-app
labels:
app: web
spec:
containers:
- name: web-app
image: hashicorp/http-echo
args:
- "-text=I am the Web API"
---
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: web-service
spec:
selector:
app: web
ports:
- port: 5678
mobile-echo.yaml
kind: Pod
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: mobile-app
labels:
app: mobile
spec:
containers:
- name: mobile-app
image: hashicorp/http-echo
args:
- "-text=I am the Mobile API"
---
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: mobile-service
spec:
selector:
app: mobile
ports:
- port: 5678
Create those two YAML files and create those apps in Kubernetes:
kubectl apply -f web-echo.yaml
kubectl apply -f mobile-echo.yaml
Creating the Ingress
Now we need to declare an Ingress to route requests to /web to the first service, and requests to /mobile to second:
nginx-ingress.yaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress
annotations:
ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /web
backend:
serviceName: web-service
servicePort: 5678
- path: /mobile
backend:
serviceName: mobile-service
servicePort: 5678
Create the Ingress using the Kubernetes command:
kubectl create -f nginx-ingress.yaml
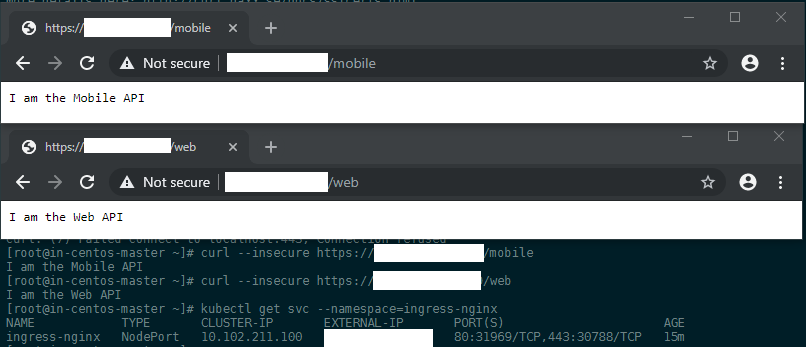
Testing the Ingress
You should now be able to see that the service was created with kubectl get svc --namespace=ingress-nginx and access your two apps via the WAN IP of your Kubernetes Master (see remark above about the externalIP):
Adding a Node.js / Express.js Web App
We earlier created a Node.js Web App that uses Express.js to host web content and wrapped it into an Docker container. I want to try to add this docker image and use the web app behind the NGINX Ingress.
For this app we used the Express Generator to scaffold a simple website that consist of 2 pages - one hosted on the app root /, the other one under /users - Github Repository. This was set up inside the app.js file the following way:
var indexRouter = require('./routes/index');
var usersRouter = require('./routes/users');
...
app.use('/', indexRouter);
app.use('/users', usersRouter);
We are importing a router that is responsible for a specific route. The router itself - e.g. in case of the /users route just replies with a string once sends a GET:
var express = require('express');
var router = express.Router();
/* GET users listing. */
router.get('/', function(req, res, next) {
res.send('User Login');
});
module.exports = router;
Preparing the NGINX Ingress
We can now add the app to our Ingress configuration as follows:
nginx-ingress.yaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress
annotations:
ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /web
backend:
serviceName: web-service
servicePort: 5678
- path: /mobile
backend:
serviceName: mobile-service
servicePort: 5678
- path: /test
backend:
serviceName: test-service
servicePort: 3000
We just added a third route to the Ingress on /test and assigned the service port that our Express app is running on - the port for the app is defined in .\bin\www :
var port = normalizePort(process.env.PORT || '3000');
Great now we could push the app to Docker Hub - e.g. to mpolinowski/docker-node-express - and create the following Pod and Service configuration for it:
kind: Pod
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: web-app
labels:
app: web
spec:
containers:
- name: web-app
image: mpolinowski/docker-node-express
ports:
- containerPort: 3000
---
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: web-service
spec:
selector:
app: web
ports:
- port: 3000
And run it and access our app on the Master servers WAN IP with the URL /test ....
It could be so easy, but...
You will get a 404 from NGINX - the Ingress is working (good!), but there is nothing hosting on that URL. What went wrong here is the Path Prefix is messing with our app routing. /test should lead us to the root of our web app - at least that is what I expected (this is how the router in Express.js works). But Ingress just recognizes that /test belongs to our web app and then routes /test to it. Since we only have the / and /users route defined, this leads us to a 404 from NGINX.
To fix this, we have to go back to the app.js of our web app and add the Path Prefix to every route:
app.use('/test', indexRouter);
app.use('/test/users', usersRouter);
Now rebuilding the Docker image, re-uploading it to Docker Hub and restarting the image in Kubernetes gives us the result we needed:
We added the NGINX Ingress to our Kubernetes cluster and used NGINX to proxy three web apps that can now be reached over the internet under the routes <Cluster WAN IP>\web, <Cluster WAN IP>\mobile, <Cluster WAN IP>\test
Adding TLS
You can create a certificate for your domain using Certbot. This will create two files that we need to add as a secret to Kubernetes - privkey.pem and fullchain.pem. Both files can be found under /etc/letsencrypt/live/my.domain.com and be added with the following command:
kubectl create secret tls my-secret --key ./privkey.pem --cert ./fullchain.pem
And change the Ingress configuration to use the certificate:
nginx-ingress.yaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress
annotations:
ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- my.domain.com
secretName: my-domain-secret
rules:
- host: my.domain.com
http:
paths:
- path: /web
backend:
serviceName: web-service
servicePort: 5678
- path: /mobile
backend:
serviceName: mobile-service
servicePort: 5678
- path: /test
backend:
serviceName: test-service
servicePort: 3000