Working with SQL Dumps

Exporting/Importing SQL files
mysqldump -u username -p database_name > file.sql
mysql -u username -p database_name < file.sql
MySQL Docker Container
We can start the MySQL database on our system using Docker. Download the MySQL Container by typing docker pull mysql into your Terminal / Powershell. To start the container run the following commands:
docker volume create crv_mysql
docker run \
-e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=my-secret-pw \
-e MYSQL_DATABASE=devdb \
-e MYSQL_USER=dbuser \
-e MYSQL_PASSWORD=dbpassword \
--mount type=volume,src=crv_mysql,dst=/var/lib/mysql \
-p 3306:3306 \
-d \
mysql:latest
This will create a volume to store your data in /var/lib/mysql and also create a non-root user and a database that can be accessed with this user. If you just need a quick look at an SQL dump, simplify this command to:
docker run \
-e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=my-secret-pw \
-e MYSQL_PASSWORD=dbpassword \
-p 3306:3306 \
-d \
mysql:latest
You can no connect to the database with root and dbpassword on 127.0.0.1:3306.
HeidiSQL
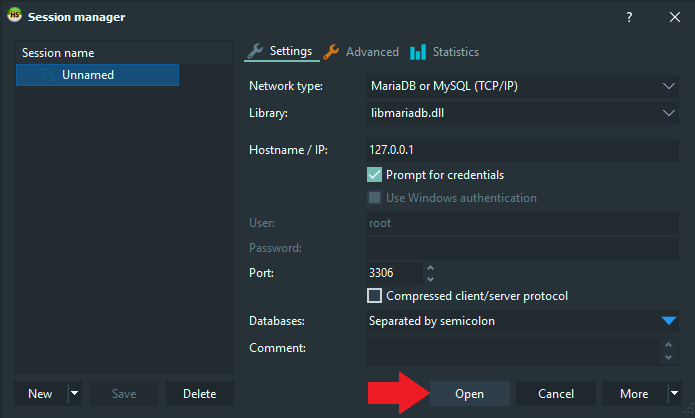
Under Windows we can use HeidiSQL to work with our database. Once you downloaded and installed the software connect the software with the database service:
Now right-click to add a new database. Once created select the database and click on the folder icon to add your SQL file: