React.js with Typescript 2023

- Foundation
- Typescript Basics
- React Typescript
- Styling React
- React Router
- Redux State Management
- RESTful APIs
- Video Embedding
Foundation
- Vite.js:
npm create vite@latest react-ts -- --template react-swc-ts - TailwindCSS:
npm install -D tailwindcss postcss autoprefixer - ShadCN UI:
npx shadcn-ui@latest init - React Router:
npm install react-router-dom - Lucide Icons:
npm install lucide-react - Performant, flexible and extensible forms with easy-to-use validation.:
npm install react-hook-form - Redux State Management:
npm i @reduxjs/toolkit react-redux
Typescript Basics
Type Declaration
Assigning types when declaring variables:
let flag: boolean;
const numbers: number[] = [];
let lastOrder: Date | null;
lastOrder = new Date();
In objects optional variables can be assigned types using a ?:
const productA: { name: string; unitPrice?: number } = {
name: "Product A",
};
Handling types in functions:
function getTotal(
unitPrice: number,
quantity: number,
discount: number
): number {
const priceWithoutDiscount = unitPrice * quantity;
const discountAmount = priceWithoutDiscount * discount;
return priceWithoutDiscount - discountAmount;
}
Use unknown instead of any to be able to widen the type once it's type becomes defined:
fetch("https://swapi.dev/api/people/1")
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((data: unknown) => {
if (isCharacter(data)) {
console.log("name", data.name);
}
});
function isCharacter(
character: any
): character is { name: string } {
return "name" in character;
}
Use void instead of undefined for functions that don't have a return statement:
function logText(text: string): void {
console.log(text);
}
Function with unreachable return statements should use never instead:
function taskLoop(taskName: string): never {
while (true) {
console.log(`${taskName} is running...`);
}
}
Working with classes:
class Product {
constructor(public name: string, public unitPrice: number) {
this.name = name;
this.unitPrice = unitPrice;
}
getDiscountedPrice(discount: number): number {
return this.unitPrice - discount;
}
}
const productA = new Product("Product A", 45);
console.log(productA.getDiscountedPrice(5));
Aliases
To clean-up the type declaration we can use aliases:
type Product = { name: string; unitPrice?: number };
type DiscountedProduct = Product & { discount: number };
let productA: Product = { name: "Product A" };
let productB: DiscountedProduct = { name: "Product B", unitPrice: 299, discount: 15 };
Using type aliases to represent functions:
type Purchase = (quantity: number) => void;
type Product = {
name: string;
unitPrice?: number;
purchase: Purchase;
};
let productA: Product = {
name: "Product A",
purchase: (quantity) =>
console.log(`${quantity} Product A sold.`),
};
table.purchase(4);
Interfaces
Interfaces instead of type aliases:
interface Product {
name: string;
unitPrice?: number;
}
interface DiscountedProduct extends Product {
discount: number;
}
interface Purchase {(quantity: number): void}
interface Product {
name: string;
unitPrice?: number;
purchase: Purchase;
}
let productA: Product = {
name: "Product A",
purchase: (quantity) =>
console.log(`${quantity} Product A sold.`),
};
productA.purchase(4);
Enumerations
You can use union types to declare sets of allowed names:
type Colour = "red" | "green" | "blue";
let colour: Colour = "red";
console.log(colour);
Enumerations allow the declaration of sets like:
enum Level {
Info,
Warning,
Error
}
let level = Level.Info;
console.log(level);
let level = Level[1];
console.log(level);
enum Level {
Low = "L",
Medium = "M",
High = "H"
}
let level = Level.High;
console.log(level);
React Typescript
Effect Hook
The effect Hook is used to execute component side effects when a component is rendered or when certain props or states change.
import { useEffect, useState } from "react";
export function EffectHookClick() {
const [clicked, setClicked] = useState(false);
useEffect(() => {
if (clicked) {
console.log("INFO :: Effect Hooked");
}
}, [clicked]);
function handleClick() {
setClicked(true);
}
return <button onClick={handleClick}>Cause effect</button>;
}
function EffectHookCondition({someProp}) {
useEffect(() => {
if (someProp) {
console.log("Some effect");
}
});
if (!someProp) {
return null
}
return
}
function EffectHookReturnFunction({ onClickAnywhere }) {
useEffect(() => {
function handleClick() {
onClickAnywhere();
}
document.addEventListener("click", listener);
return () => {
document.removeEventListener("click", listener);
};
});
return
}
Data Fetching
A common use case for the effect Hook is fetching data:
import { useEffect } from 'react';
type Person = {
name: string,
};
export function simAPIRequest(): Promise<Person> {
return new Promise((resolve) =>
setTimeout(() => resolve({ name: "George González" }), 1000)
);
}
export function DisplayAPIResponse() {
useEffect(() => {
simAPIRequest().then((person) => console.log(person));
}, []);
return null;
}
State Hook
State hooks can be used to store and update state. E.g. you can write the API response from above into a state variable:
export function DisplayAPIResponse() {
const [name, setName] = useState<string | undefined>();
const [score, setScore] = useState(0);
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true);
useEffect(() => {
simAPIRequest().then((person) => {
setLoading(false);
setName(person.name);
});
}, []);
if (loading) {
return <div>Loading ...</div>;
}
return (
<div>
<h3>{name}, {score}</h3>
<button onClick={() => setScore(score + 1)}>Add</button>
<button onClick={() => setScore(score - 1)}>Subtract</button>
<button onClick={() => setScore(0)}>Reset</button>
</div>
);
}
Ref Hook
useRef returns a variable whose value is persisted for the lifetime of a component:
const ref = useRef<Ref>(initialValue);
ref.current = newValue;
console.log("Current ref value", ref.current);
import { useRef } from "react";
export function InputComponent() {
const inputRef = useRef<HTMLInputElement>(null);
function logInput() {
console.log(inputRef.current);
}
return <input ref={inputRef} onChange={logInput} type="text" />;
}
Use a ref hook to focus a HTML element after a component is loaded:
const addButtonRef = useRef<HTMLButtonElement>(null);
useEffect(() => {
if (!loading) {
addButtonRef.current?.focus();
}
}, [loading]);
return (
<button ref={addButtonRef}>Add</button>
);
Memo Hook
Memo Hooks can be used to store values that have computationally expensive calculations. E.g. the following value is recalculated every time the variable a or b change:
import { useMemo } from 'react';
const memoValue = useMemo<number>(
() => thisWillTakeAWhile(a, b),
[a, b]
);
As long as a and b don't change the calculation is only done once when the component is loaded:
function calculateScore() {
console.log("INFO :: Score is being calculated.");
let sum = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}
const getScore = useMemo(
() => calculateScore(),
[]
);
return (
<p>{getScore}</p>
);
Callback Hook
While the Memo Hook is used to cache values the Callback Hook holds an entire function. The memo function wraps the component and memoizes the result for a given set of props preventing unnecessary re-rendering of slow components:
const memoizedValue = useCallback< () => void > (
() => someFunction (),
[]
);
Styling React
Vanilla CSS
import './App.css';
function App() {
return (
<div className="App">
...
</div>
);
}
Tailwind CSS
Install tailwindcss and its peer dependencies, then generate your tailwind.config.js and postcss.config.js files:
npm install -D tailwindcss postcss autoprefixer
npx tailwindcss init -p
Created Tailwind CSS config file: tailwind.config.js
Created PostCSS config file: postcss.config.js
And add the following code to the tsconfig.json file to resolve paths:
{
"compilerOptions": {
// ...
"baseUrl": ".",
"paths": {
"@/*": [
"./src/*"
]
}
// ...
}
}
Add the following code to the vite.config.ts so your app can resolve paths without error:
# (so you can import "path" without error)
npm i -D @types/node
npm i @vitejs/plugin-react
import path from "path"
import react from "@vitejs/plugin-react"
import { defineConfig } from "vite"
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [react()],
resolve: {
alias: {
"@": path.resolve(__dirname, "./src"),
},
},
})
ShadCN UI
Run the shadcn-ui init command to setup your project:
npx shadcn-ui@latest init
You will be asked a few questions to configure components.json:
Would you like to use TypeScript (recommended)? no / yes
Which style would you like to use? › Default
Which color would you like to use as base color? › Slate
Where is your global CSS file? › › src/index.css
Do you want to use CSS variables for colors? › no / yes
Where is your tailwind.config.js located? › tailwind.config.js
Configure the import alias for components: › @/components
Configure the import alias for utils: › @/lib/utils
Are you using React Server Components? › no / yes (no)
You can now start adding components to your project.
npx shadcn-ui@latest add button
The command above will add the Button component to your project. You can then import it like this:
import { Button } from "@/components/ui/button"
export default function Home() {
return (
<div>
<Button>Click me</Button>
</div>
)
}
Importing SVGs
npm install --save-dev vite-plugin-svgr
Add the following to tsconfig.json:
{
"compilerOptions": {
"types": ["vite/client", "vite-plugin-svgr/client"],
And import the plugin to vite.config.ts:
import svgr from "vite-plugin-svgr";
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [
svgr()
],
You can now import SVGs like:
import AlertIcon from "@/assets/alert-triangle.svg?react";
...
return (
<AlertIcon />
React Router
npm i react-router-dom
Prepare a set of nested routes for your app. Here all pages will be rendered as children inside the App component:
@/routes/Routes.tsx
import {
createBrowserRouter,
RouterProvider,
Navigate
} from 'react-router-dom';
import { App } from '@/App'
import { FrontPage } from '@/pages/Frontpage';
import { CameraList } from '@/pages/Camera_List';
const router = createBrowserRouter(
[{
path: '/',
element: <App />,
errorElement: <ErrorPage />,
children: [
{
path: 'dashboard',
element: <FrontPage />,
},
{
path: 'camera-list',
element: <CameraList />,
},
{
path: '*',
element: <Navigate to="dashboard" replace />,
},
]}
]);
export function Routes() {
return <RouterProvider router={router} />;
}
The App component only contains an Outlet for the child components and components you want to be displayed on all pages - navigation bars, side navigation, etc.:
@/App.tsx
import { Outlet } from 'react-router-dom';
import { NavBar } from '@/components/NavBar'
export function App() {
return (
<>
<NavBar />
<Outlet />
</>
);
}
The routes are now imported into Main:
@/main.tsx
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client'
import { Routes } from '@/routes/Routes'
import { ThemeProvider } from "@/components/Theme-Provider"
import '@/styles/index.css'
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root')!).render(
<React.StrictMode>
<ThemeProvider defaultTheme="dark" storageKey="vite-ui-theme">
<Routes />
</ThemeProvider>
</React.StrictMode>,
)
Route Parameter
Add another route that selects a single camera by ID:
@/routes/Routes.tsx
{
path: 'camera/:id',
element: <CameraPage />,
},
Mock an API request to retrieve the camera information:
@/data/cameras.ts
export type Camera = {
id: number;
name: string;
recordings: number;
ip: string;
};
export const cameras: Camera[] = [
{
id: 0,
name: 'IN-9420 2K+ WQHD',
recordings: 21,
ip: '192.168.2.21',
},
...
Retrieve camera ID from the URL parameter and find the camera in the list above to display its details:
@/pages/CameraPage.tsx
import { useParams, Link } from 'react-router-dom';
type Params = {
id: string;
};
export function CameraPage() {
const params = useParams<Params>();
// get camera ID from URL param
const id = params.id === undefined ? undefined : parseInt(params.id)
// find corresponding camera
const camera = cameras.find(
(camera) => camera.id === id
)
return (
<div className="text-center p-5 text-xl">
{camera === undefined ? (
<h1 className="text-xl">
ERROR :: Camera not available
</h1>
) : (
<>
<h1 className="text-xl">
Camera Name: {camera.name}
</h1>
<p className="text-base">
Camera IP: {camera.ip}
</p>
<p className="text-base">
Recordings: {camera.recordings}
</p>
</>
)}
</div>
)}
Lazy Loading
To lazy load 'heavy' pages add suspense to the route definition:
import { lazy, Suspense } from 'react'
import { App } from '@/App'
import { ErrorPage } from '@/pages/ErrorPage'
const Dashboard = lazy(() => import('@/pages/Dashboard'));
const router = createBrowserRouter(
[{
path: '/',
element: <App />,
errorElement: <ErrorPage />,
children: [
{
path: 'dashboard',
element: (
<Suspense fallback={
<div>
Loading...
</div>
}>
<Dashboard />
</Suspense>
)
}
...
React Router Form
import {
Form,
ActionFunctionArgs,
redirect,
} from 'react-router-dom';
import { Button } from "@/components/ui/button"
import {
Card,
CardContent,
CardDescription,
CardHeader,
CardTitle,
} from "@/components/ui/card"
import { Input } from "@/components/ui/input"
import { Label } from "@/components/ui/label"
type LoginType = {
name: string;
password: string;
}
export function LoginForm() {
return (
<div className='container mx-auto h-screen flex justify-center'>
<Card className="w-fit h-fit mt-16">
<CardHeader>
<CardTitle>Login</CardTitle>
<CardDescription>Please use your user login to access your cameras.</CardDescription>
</CardHeader>
<CardContent>
<Form method="post" className="space-y-8">
<div className="grid w-full max-w-sm items-center gap-1.5">
<Label htmlFor="name">Username</Label>
<Input type="text" id="name" name="name" placeholder="Username" required />
</div>
<div className="grid w-full max-w-sm items-center gap-1.5">
<Label htmlFor="password">Password</Label>
<Input type="password" id="password" name="password" placeholder="Password" required />
</div>
<div>
<Button type="submit">
Submit
</Button>
</div>
</Form>
</CardContent>
</Card>
</div>
);
}
export async function loginFormAction({ request }: ActionFunctionArgs) {
const formData = await request.formData();
const login = {
name: formData.get('name'),
password: formData.get('password'),
} as LoginType;
console.log('Login details:', login);
return redirect(`/start/`);
}
import { App } from '@/App'
import { ErrorPage } from '@/pages/ErrorPage'
import { Welcome } from '@/pages/Welcome'
import { loginFormAction } from '@/components/welcome/Login'
const router = createBrowserRouter(
[{
path: '/',
element: <App />,
errorElement: <ErrorPage />,
children: [
{
index: true,
element: <Welcome />,
action: loginFormAction,
},
...
Form Hooks
npm install react-hook-form`
import { useForm, FieldError } from 'react-hook-form';
import { useNavigate } from 'react-router-dom';
import { Button } from "@/components/ui/button"
import {
Card,
CardContent,
CardDescription,
CardHeader,
CardTitle,
} from "@/components/ui/card"
import { Input } from "@/components/ui/input"
import { Label } from "@/components/ui/label"
import { Textarea } from "@/components/ui/textarea"
import { ValidationError } from '@/components/create_user/ValidationError'
type UserType = {
name: string;
password: string;
email?: string;
level: string;
notes?: string;
}
export function UserForm() {
const {
register,
handleSubmit,
formState: { errors, isSubmitting }
} = useForm<UserType>({
mode: "onBlur",
reValidateMode: "onBlur"
})
const navigate = useNavigate()
function onSubmit(user: UserType) {
console.log('Submitted details:', user);
navigate(`/user-details/${user.name}`);
}
function getEditorStyle(fieldError: FieldError |
undefined) {
return fieldError ? 'border-red-500' : '';
}
return (
<div className='container mx-auto h-screen flex justify-center'>
<Card className="w-fit h-fit mt-4">
<CardHeader>
<CardTitle>Add a User</CardTitle>
<CardDescription>Fill out the username, password and access level to create a new user.</CardDescription>
</CardHeader>
<CardContent>
<form noValidate onSubmit={handleSubmit(onSubmit)}>
<div>
<Label htmlFor="name">Your user name</Label>
<Input
type="text"
id="name"
disabled={isSubmitting}
{...register('name', {
required: 'You must enter your name.',
})}
className={getEditorStyle(errors.name)}
/>
<ValidationError fieldError={errors.name} />
</div>
<div className='mt-4'>
<Label htmlFor="password" className='my-4'>Your user password</Label>
<Input
type="password"
id="password"
disabled={isSubmitting}
{...register('password', {
required: 'You must enter your password.',
})}
className={getEditorStyle(errors.password)}
/>
<ValidationError fieldError={errors.password} />
</div>
<div className='mt-4'>
<Label htmlFor="email" className='my-2'>Your email address</Label>
<Input
type="email"
id="email"
disabled={isSubmitting}
{...register('email', {
pattern: {
value: /\S+@\S+\.\S+/,
message: 'Entered value does not match email format.',
},
})}
className={getEditorStyle(errors.email)}
/>
<ValidationError fieldError={errors.email} />
</div>
<div className='mt-4'>
<Label htmlFor="level" className='my-2'>Granted access level</Label>
<div className='flex flex-col'>
<select
id="level"
disabled={isSubmitting}
{...register('level', {
required: 'You must enter the authorization level.',
})}
className='flex h-9 w-full items-center justify-between whitespace-nowrap rounded-md border border-input bg-transparent px-3 py-2 text-sm shadow-sm ring-offset-background placeholder:text-muted-foreground focus:outline-none focus:ring-1 focus:ring-ring disabled:cursor-not-allowed disabled:opacity-5'
>
<option value="">Select an authorization level...</option>
<option value="user">User</option>
<option value="operator">Operator</option>
<option value="administrator">Administrator</option>
</select>
<ValidationError fieldError={errors.level} />
</div>
</div>
<div className='mt-4'>
<Label htmlFor="notes">Additional notes</Label>
<Textarea id="notes" disabled={isSubmitting} {...register('notes')} />
</div>
<div className='mt-4'>
<Button type="submit">
Submit
</Button>
</div>
</form>
</CardContent>
</Card>
</div>
);
}
import { FieldError } from 'react-hook-form';
type Props = {
fieldError: FieldError | undefined;
};
export function ValidationError({ fieldError }: Props) {
if (!fieldError) {
return null;
}
return (
<div role="alert" className="text-red-500 text-xs mt-1">
{fieldError.message}
</div>
);
}
Redux State Management
Store
Create a store using the Redux Toolkit:
@/store/store.tsx
import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';
import userReducer from './userSlice';
export const store = configureStore({
reducer: {
user: userReducer,
camera: cameraReducer,
},
});
// ReturnType infers the type of the full state object
export type RootState = ReturnType<typeof store.getState>;
Every app feature has its own slice of the state accessible by its own reducer function:
@/store/userSlice.tsx
import { createSlice } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
import type { PayloadAction } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
// mocked API request to get current user - see below
import { User } from '@/api/authenticate'
type State = {
user: undefined | User;
permissions: undefined | string[];
loading: boolean;
}
const initialState: State = {
user: undefined,
permissions: undefined,
loading: false,
}
export const userSlice = createSlice({
name: 'user',
initialState,
reducers: {
authenticateAction: (state) => {
state.loading = true;
},
authenticatedAction: (state, action: PayloadAction<User | undefined>) => {
state.user = action.payload;
state.loading = false;
},
authorizeAction: (state) => {
state.loading = true;
},
authorizedAction: (state, action: PayloadAction<string[]>) => {
state.permissions = action.payload;
state.loading = false;
},
},
})
export const { authenticateAction, authenticatedAction, authorizeAction, authorizedAction } =
userSlice.actions
export default userSlice.reducer
The Redux store needs to be provided to our React component tree:
@/App.tsx
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
import { Outlet } from 'react-router-dom';
import { NavBar } from '@/components/navbar/NavBar'
import { store } from '@/store/store';
export function App() {
return (
<>
<Provider store={store}>
<NavBar />
<Outlet />
</Provider>
</>
);
}
Select State
@/components/navbar/NavBar.tsx
import { useSelector, useDispatch } from 'react-redux'
import { authenticate } from '@/api/authenticate'
import { authorize } from '@/api/authorize'
import type { RootState } from '@/store/store'
export function NavBar() {
const user = useSelector((state: RootState) => state.user.user);
const loading = useSelector((state: RootState) => state.user.loading);
...
return (
...
<NavigationMenuItem>
{user ? (
<span className="ml-auto">Welcome back {user.name}!</span>
) : (
<Button variant="outline"
onClick={handleSignInClick}
disabled={loading}
>
{loading ? '...' : 'Sign in'}
</Button>
)}
</NavigationMenuItem>
...
Dispatch State Updates
The handleSignInClick() dispatches a sign-in request:
export function NavBar() {
...
const dispatch = useDispatch();
async function handleSignInClick() {
// set loading to true
dispatch(authenticateAction());
// get authenticated user from API
const authenticatedUser = await authenticate();
// set authenticated user to current logged in user
dispatch(authenticatedAction(authenticatedUser));
// once the user is known set its permissions
if (authenticatedUser !== undefined) {
dispatch(authorizeAction());
const authorizedPermissions = await authorize(authenticatedUser.id);
dispatch(authorizedAction(authorizedPermissions));
}
}
...
The user name and its permissions are retrieved from a mocked API request:
@/api/authenticate.ts
export type User = {
id: string;
name: string;
};
export function authenticate(): Promise<User | undefined> {
return new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(() => resolve({ id: '1', name: 'Admin' }), 1000));
}
@/api/authorize.ts
export function authorize(id: string): Promise<string[]> {
return new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(() => resolve(['admin']), 1000));
}
Working with User Roles
Conditional loading of content based on user roles:
@/components/login/Vault.tsx
import { useSelector } from 'react-redux'
import { RootState } from '@/store/store'
type Content = {
children: JSX.Element
}
export function Vault({ children }: Content) {
// get array of permissions for current user
const permissions = useSelector((state: RootState) => state.user.permissions);
// if permissions exist and include 'admin' load children
if (permissions && permissions.includes('admin')) {
return <div>{ children }</div>;
}
return <h3 className="mt-8 text-center">Please sign in to view this content!</h3>;
}
Wrap all sensitive components inside a Vault instance:
import { Vault } from '@/components/login/Vault'
export function PageComponent() {
return (
<Vault>
<div className="App">
...
</div>
</Vault>
);
}
RESTful APIs
Data for a JSON mock API:
api.json
{
"events": [
{
"uuid": "90080d52-f2ac-46e1-ad1e-ec7d6ab304a1",
"title": "#6534 Entrance Left",
"description": "2023-12-26 15:51:32: [Alarm]: Motion in area [1]"
},
{
"uuid": "c8ada1fe-318b-43a4-adc5-367d526cc5dd",
"title": "#6533 Lobby",
"description": "2023-12-26 15:50:38: [Event]: admin has logged in from 192.168.2.112"
},
{
"uuid": "762ad93a-4bcc-4f8d-97d1-93d4f1da1f35",
"title": "#6456 Elevator",
"description": "2023-12-26 15:44:19: [Event]: Switching to night mode"
}
]
}
Requirements:
npm i -D json-servernpmstart script inpackage.json
{
...,
"scripts": {
...,
"api": "json-server --watch api.json --port 8080 --delay 2500"
},
...
}
Execute the script and verify that the API is accessible:
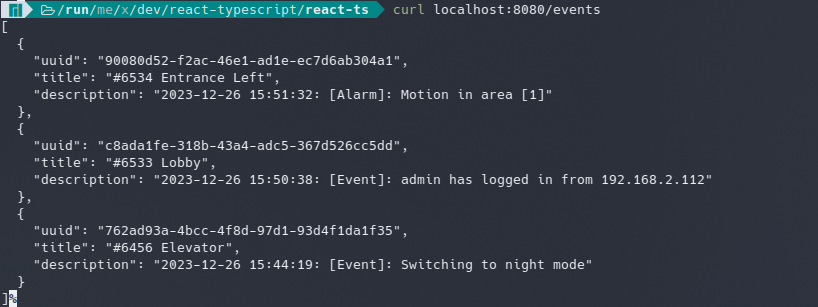
Vite.js Environment Variables: To prevent accidentally leaking env variables to the client, only variables prefixed with VITE_ are exposed to your Vite-processed code. e.g.:
.env
VITE_API_URL = http://localhost:8080/events/
The URL is now exposed:
console.log(import.meta.env.VITE_API_URL)
To get TypeScript IntelliSense for user-defined env variables you can create an env.d.ts in src directory, then augment ImportMetaEnv like this:
@/env.d.ts
/// <reference types="vite/client" />
interface ImportMetaEnv {
readonly VITE_API_URL: string
// more .env variables...
}
interface ImportMeta {
readonly env: ImportMetaEnv
}
Effect Fetching
Get JSON data from your API:
@/components/reports/GetReports.ts
export type ReportData = {
uuid: number;
title: string;
description: string;
}
export async function getReports() {
const response = await fetch(
// add '!' to assert that expression can’t be null or undefined
import.meta.env.VITE_API_URL!
);
const body = (await response.json()) as unknown
// type assertion for API response
assertIsReports(body);
return body;
}
export function assertIsReports(
reportData: unknown
): asserts reportData is ReportData[] {
if (!Array.isArray(reportData)) {
throw new Error("ERROR :: Report isn't an array");
}
if (reportData.length === 0) {
return
}
reportData.forEach((report) => {
if (!('uuid' in report)) {
throw new Error("ERROR :: Report doesn't contain an UUID");
}
if (typeof report.uuid !== 'string') {
throw new Error('ERROR :: UUID is not a string');
}
if (!('title' in report)) {
throw new Error("ERROR :: Report doesn't contain title");
}
if (typeof report.title !== 'string') {
throw new Error('ERROR :: Title is not a string');
}
if (!('description' in report)) {
throw new Error("ERROR :: Report doesn't contain description");
}
if (typeof report.description != 'string') {
throw new Error('ERROR :: Description is not a string');
}
})
}
The fetched JSON data can now be displayed in the report list component:
@/components/reports/ReportList.tsx
import {
import {
Card,
CardContent,
CardDescription,
CardHeader,
CardTitle,
} from "@/components/ui/card"
import {
Table,
TableBody,
TableCaption,
TableCell,
TableHead,
TableHeader,
TableRow,
} from "@/components/ui/table"
import { ReportData } from './GetReports'
type Props = {
reports: ReportData[];
}
export function ReportList({ reports }: Props) {
return (
<Card className="w-3/4">
<CardHeader>
<CardTitle>Surveillance Log</CardTitle>
<CardDescription>Recorded camera events</CardDescription>
</CardHeader>
<CardContent>
<Table>
<TableCaption>Latest Events</TableCaption>
<TableHeader>
<TableRow>
<TableHead>Camera</TableHead>
<TableHead>Description</TableHead>
</TableRow>
</TableHeader>
<TableBody>
{reports.map((report) => (
<TableRow key={report.uuid}>
<TableCell className="font-bold text-left">{report.title}</TableCell>
<TableCell className="text-left">{report.description}</TableCell>
</TableRow>
))}
</TableBody>
</Table>
</CardContent>
</Card>
)
}
The list view can now be used in any page:
import { useEffect, useState } from 'react';
import { getReports, ReportData } from '@/components/reports/GetReports'
import { ReportList } from '@/components/reports/ReportList'
export function ReportPage() {
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(true)
const [reports, setReports] = useState<ReportData[]>([])
useEffect(() => {
let cancel = false
// fetch data from api
getReports().then((data) => {
if (!cancel) {
setReports(data);
setIsLoading(false);
}
})
// cancel load if component is unmounted
return () => {
cancel = true;
}
}, []);
if (isLoading) {
return (
<div className="w-96 mx-auto mt-6">
Loading ...
</div>
);
}
return (
...
<ReportList reports={reports} />
...
);
}
Effect Posting
@/components/reports/NewReport.ts
export type NewReportData = {
title: string;
description: string;
}
export type SavedReportData = {
uuid: string;
}
export async function savePost( newReportData: NewReportData ) {
const response = await fetch(
import.meta.env.VITE_API_URL!,
{
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify(newReportData),
headers: {'Content-Type': 'application/json'}
}
)
const body = (await response.json()) as unknown;
assertIsSavedReport(body);
return { ...newReportData, ...body };
}
function assertIsSavedReport( post: any ):
asserts post is SavedReportData {
if (!('uuid' in post)) {
throw new Error("ERROR :: Post doesn't contain an uuid")
}
if (typeof post.uuid !== 'number') {
throw new Error('ERROR :: uuid is not a number');
}
}
React Router Data Loading
Use React Router to get the data before it renders a component defined on the route. This can be done by adding the getReports function as a loader:
import {
createBrowserRouter,
RouterProvider,
Navigate,
defer
} from 'react-router-dom';
import { CameraPage } from '@/pages/CameraPage'
import { getReports } from '@/components/reports/GetReports'
const router = createBrowserRouter(
[{
...
{
path: 'camera/:id',
element: <CameraPage />,
loader: async () => defer({ reports: getReports() })
},
...
The data is now fetched when the route is triggered and made available to our component via a useLoaderData hook::
@/pages/CameraPage.tsx
import { Suspense } from 'react'
import {
useParams,
useLoaderData,
Await,
Link
} from 'react-router-dom'
import { ReportList } from '@/components/reports/ReportList'
import { assertIsReports } from '@/components/reports/GetReports'
import { ReportData } from '@/components/reports/types'
export function CameraPage() {
...
// get camera reports from react-router route
const data = useLoaderData()
assertIsData(data)
return (
...
<CardContent>
<Suspense fallback={<div>Fetching...</div>}>
<Await resolve={data.reports}>
{(reports) => {
assertIsReports(reports)
return <ReportList reports={reports} />
}}
</Await>
</Suspense>
</CardContent>
...
)}
type Data = {
reports: ReportData[];
}
export function assertIsData(data: unknown): asserts data is Data {
if (typeof data !== 'object') {
throw new Error("ERROR :: Sent report data isn't an object");
}
if (data === null) {
throw new Error('ERROR :: Report data is null');
}
if (!('reports' in data)) {
throw new Error("ERROR :: data doesn't contain reports");
}
}
Video Embedding
hls Streams
npm install react-hls-player
@/components/video_streamer/HLSPlayer.tsx
import ReactHlsPlayer from 'react-hls-player'
export function HLSPlayer( href: { url: string } ) {
return (
<>
<ReactHlsPlayer
src={href.url.toString()}
autoPlay={false}
controls={true}
width="100%"
height="auto"
hlsConfig={{
maxLoadingDelay: 4,
minAutoBitrate: 0,
lowLatencyMode: true,
}}
/>
</>
);
}
@/components/video_streamer/VideoWall.tsx
import { HLSPlayer } from '@/components/video_player/HLSPlayer'
const href: URL = new URL("https://bitdash-a.akamaihd.net/content/sintel/hls/playlist.m3u8")
export function VideoWall() {
return (
<Card className="mt-12">
<CardHeader>
<CardTitle>Camera Live Video</CardTitle>
<CardDescription>Embedded HLS stream unsing hls.js</CardDescription>
</CardHeader>
<CardContent>
<div className="grid grid-flow-row-dense grid-cols-3 grid-rows-3 gap-2">
<div className="col-span-2 row-span-2">
<HLSPlayer url={href} />
</div>
...
Video File Playback
npm install video.js
npm install -D @types/video.js
@/components/video_player/VideoPlayer
import { useRef, useEffect } from 'react'
import videojs from 'video.js'
import 'video.js/dist/video-js.css'
export const VideoPlayer = (props) => {
const videoRef = useRef(null)
const playerRef = useRef(null)
const {options, onReady} = props;
useEffect(() => {
// Make sure Video.js player is only initialized once
if (!playerRef.current) {
// The Video.js player needs to be _inside_ the component el for React 18 Strict Mode.
const videoElement = document.createElement("video-js");
videoElement.classList.add('vjs-big-play-centered');
videoRef.current.appendChild(videoElement);
const player = playerRef.current = videojs(videoElement, options, () => {
videojs.log('player is ready');
onReady && onReady(player);
});
// You could update an existing player in the `else` block here
// on prop change, for example:
} else {
const player = playerRef.current;
player.autoplay(options.autoplay);
player.src(options.sources);
}
}, [options, videoRef]);
// Dispose the Video.js player when the functional component unmounts
useEffect(() => {
const player = playerRef.current;
return () => {
if (player && !player.isDisposed()) {
player.dispose();
playerRef.current = null;
}
};
}, [playerRef]);
return (
<div data-vjs-player>
<div ref={videoRef} />
</div>
);
}
@/components/video_player/VideoWall
import { useRef } from 'react'
import videojs from 'video.js'
import { VideoPlayer } from '@/components/video_player/VideoPlayer'
const videoJsOptions = {
autoplay: false,
controls: true,
responsive: true,
fluid: true,
sources: [
{
src: "//vjs.zencdn.net/v/oceans.mp4",
type: "video/mp4"
}
]
};
export function VideoWall(id: {camera: string}) {
const playerRef = useRef(null)
const handlePlayerReady = (player) => {
playerRef.current = player
// You can handle player events here, for example:
player.on('waiting', () => {
videojs.log('player is waiting')
})
player.on('dispose', () => {
videojs.log('player will dispose')
})
}
return (
<div className="col-span-2 row-span-2">
<VideoPlayer options={videoJsOptions} onReady={handlePlayerReady} />
</div>
);
}