Yolo App - Data Collection

- Prepare your Images and get Data
- Train your Tensorflow Model
- Use your Model to do Predictions
- Use Tesseract to Read Number Plates
- Flask Web Application
- Yolo v5 - Data Prep
Project Setup
Create a dependencies.txt file and install all dependencies:
opencv-python==4.5.5.62
tensorflow-gpu==2.8.0
notebook
pandas
numpy
matplotlib
sklearn
pytesseract
Note: that I am using GPU accelerated version of Tensorflow for Nvidia GPUs. Replace tensorflow-gpu with tensorflow if you don't have a compatible graphic card in your PC.
pip install -r dependencies.txt
Verify that OpenCV and Tensorflow was installed by creating and executing test.py:
import cv2
import tensorflow as tf
print('Tensorflow Version: ' + tf.__version__)
print('OpenCV Version: ' + cv2.__version__)
python test.py
Tensorflow Version: 2.8.0
OpenCV Version: 4.5.4
Data Collection
Image Labeling
I can use Google to collect photos of cars with visible license plates. I have to label those images so that they can be used for the Tensorflow training. To lable the images we are going to use labelImg, which is a graphical image annotation tool.
pip3 install labelImg
Successfully installed PyQt5-Qt5-5.15.2 PyQt5-sip-12.9.0 labelImg-1.8.3 pyqt5-5.15.6
Start the Software from your console with labelImg and label all your trainings images:
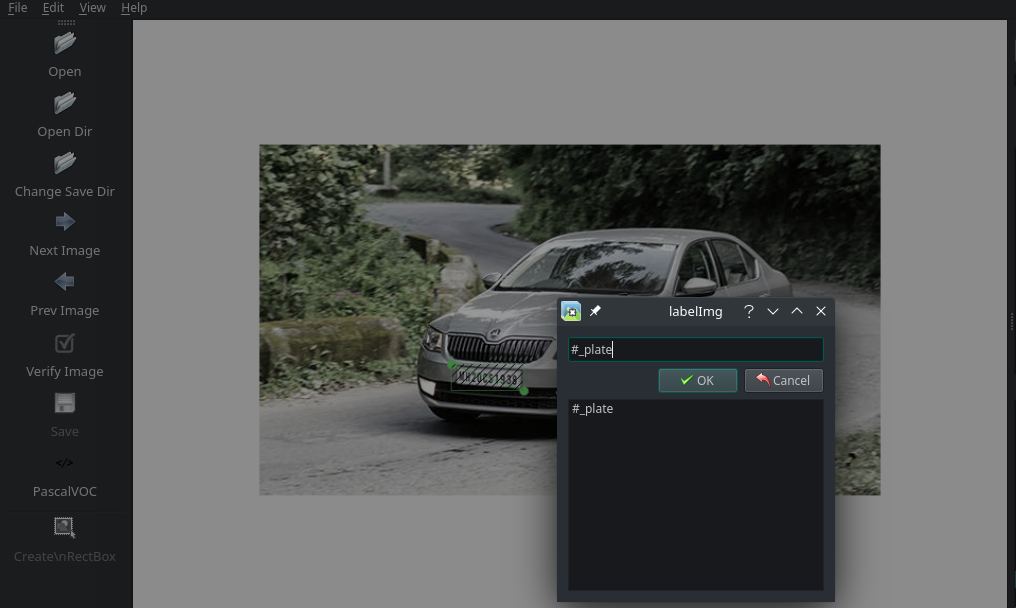
An example XML label generated by this process looks like:
<annotation>
<folder>d</folder>
<filename>N3.jpeg</filename>
<path>./resources/car.jpg</path>
<source>
<database>Unknown</database>
</source>
<size>
<width>932</width>
<height>699</height>
<depth>3</depth>
</size>
<segmented>0</segmented>
<object>
<name>num_plate</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>73</xmin>
<ymin>381</ymin>
<xmax>260</xmax>
<ymax>462</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
</annotation>
Get Bounding Boxes Coordinates
I now need to extract the Bounding Box coordinates xmin, ymin, xmax and ymax from the XML files and write them into CSV:
jupyter notebook
import pandas as pd
import xml.etree.ElementTree as xet
from glob import glob
# Get all generated image XML labels
path = glob('../labels/*.xml')
# Create empty label dictionary
labels = dict(filepath=[], xmin=[], ymin=[], xmax=[], ymax=[])
# Extract bounding box coordinates for all labels
for filename in path:
info = xet.parse(filename)
root = info.getroot()
member_object = root.find('object')
labels_info = member_object.find('bndbox')
xmin = int(labels_info.find('xmin').text)
ymin = int(labels_info.find('ymin').text)
xmax = int(labels_info.find('xmax').text)
ymax = int(labels_info.find('ymax').text)
# Append values to dictionary
labels['filepath'].append(filename)
labels['xmin'].append(xmin)
labels['ymin'].append(ymin)
labels['xmax'].append(xmax)
labels['ymax'].append(ymax)
# Create data frame from dictionary
df = pd.DataFrame(labels)
# Write data frame to CSV
df.to_csv('../labels/labels.csv')
Get Image Files for Each Bounding Box
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import xml.etree.ElementTree as xet
import os
import cv2
df = pd.read_csv('../labels/labels.csv')
# Find image file path for a given label
def getImagePath(filename):
image = xet.parse(filename).getroot().find('filename').text
image_filepath = os.path.join('../resources', image)
return image_filepath
# Select labels and find corresponding images
image_paths = list(df['filepath'].apply(getImagePath))
Draw Bounding Box on Images
To verify that everything is working we can use the bounding box coordinates to draw a rectangle onto the corresponding image:
# Get image path by index
path = image_paths[0]
img = cv2.imread(path)
# Draw bounding box onto image
# Coordinates copied from generated label
cv2.rectangle(img,(1093,645),(1396,727),(0,255,128),3)
# Make window with name Test resizeable
cv2.namedWindow('Test', cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
# Display selected image in Test window
cv2.imshow('Test', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()

Normalize Data
The models I am going to use later have been trained on a specific image size. I have to normalize all images and the generated bounding boxes to fit this requirement - e.g. an file size of 224x224 pixels:
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import load_img, img_to_array
# Get array coordinates from labels
labels = df.iloc[:,2:].values
data = []
output = []
# Loop over all images and normalize
for i in range(len(image_paths)):
# Get image path by index
image = image_paths[i]
# Get image dimensions from it' s shape
image_array = cv2.imread(image)
h,w,d = image_array.shape
# Normalize image size to fit tf model (input)
load_image = load_img(image,target_size=(224,224))
load_image_array = img_to_array(load_image)
norm_load_image_array = load_image_array/255
# Normalize coordinates from labels (output)
xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax = labels[i]
nxmin, nxmax = xmin/w, xmax/w
nymin, nymax = ymin/h, ymax/h
label_norm = (nxmin,nxmax,nymin,nymax)
# Append results to output arrays
data.append(norm_load_image_array)
output.append(label_norm)
X = np.array(data, dtype=np.float32)
Y = np.array(output, dtype=np.float32)
Divide into Training and Testing Data Set
Divide the training images and labels by a 80:20 split:
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X = np.array(data, dtype=np.float32)
Y = np.array(output, dtype=np.float32)
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, train_size=0.8, random_state=0)
Now I am ready to continue training my Tensorflow model to be able to detect license plates!