See also:
- Fun, fun, tensors: Tensor Constants, Variables and Attributes, Tensor Indexing, Expanding and Manipulations, Matrix multiplications, Squeeze, One-hot and Numpy
- Tensorflow 2 - Neural Network Regression: Building a Regression Model, Model Evaluation, Model Optimization, Working with a "Real" Dataset, Feature Scaling
- Tensorflow 2 - Neural Network Classification: Non-linear Data and Activation Functions, Model Evaluation and Performance Improvement, Multiclass Classification Problems
- Tensorflow 2 - Convolutional Neural Networks: Binary Image Classification, Multiclass Image Classification
- Tensorflow 2 - Transfer Learning: Feature Extraction, Fine-Tuning, Scaling
- Tensorflow 2 - Unsupervised Learning: Autoencoder Feature Detection, Autoencoder Super-Resolution, Generative Adverserial Networks
Tensorflow Unsupervised Learning
Generative Adverserial Networks
GANs are a framework for teaching a DL model to capture the training data’s distribution so we can generate new data from that same distribution.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense,Reshape,Dropout,LeakyReLU,Flatten,BatchNormalization,Conv2D,Conv2DTranspose
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
SEED = 42
INPUT_SHAPE = 100
BATCH_SIZE = 32
EPOCHS = 25
Dataset
Using a GAN to generate "fake" MNIST digit images.
# setting up the dataset
(X_train, y_train), (X_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
plt.imshow(X_train[8888])
plt.title(y_train[8888])
plt.show()
# to speed up the training we can pre-select
# only images with label `3`
X_train_three = X_train[y_train==3]
print(X_train_three.shape)
# there are 6131 images that represent the digit 3
# (6131, 28, 28)
# plot results
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
# ROW 1
plt.subplot(3, 3, 1)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(X_train_three[1])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 2)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(X_train_three[2])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 3)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(X_train_three[3])
# ROW 2
plt.subplot(3, 3, 4)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(X_train_three[4])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 5)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(X_train_three[5])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 6)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(X_train_three[6])
# ROW 3
plt.subplot(3, 3, 7)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(X_train_three[7])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 8)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(X_train_three[8])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 9)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(X_train_three[9])

Create Batched Dataset
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(X_train_three).shuffle(buffer_size=1000)
dataset = dataset.batch(BATCH_SIZE, drop_remainder=True).prefetch(1)
Building the Model
Generator
tf.random.set_seed(SEED)
generator = Sequential(name="generator")
generator.add(Dense(100, activation="relu", input_shape=[INPUT_SHAPE]))
generator.add(Dense(150,activation='relu'))
generator.add(Dense(784, activation="sigmoid")) # 28*28 = 784
generator.add(Reshape([28,28]))
Discriminator
discriminator = Sequential(name="discriminator")
discriminator.add(Flatten(input_shape=[28,28]))
discriminator.add(Dense(150,activation='relu'))
discriminator.add(Dense(100,activation='relu'))
discriminator.add(Dense(1,activation="sigmoid"))
discriminator.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", optimizer="adam")
discriminator.trainable = False
GAN = Sequential([generator, discriminator])
GAN.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", optimizer="adam")
GAN.summary()
# Model: "sequential"
# _________________________________________________________________
# Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
# =================================================================
# generator (Sequential) (None, 28, 28) 143634
# discriminator (Sequential) (None, 1) 132951
# =================================================================
# Total params: 276,585
# Trainable params: 143,634
# Non-trainable params: 132,951
# _________________________________________________________________
Training the Model
# Grab the seprate components
generator, discriminator = GAN.layers
# For every epcoh
for epoch in range(EPOCHS):
print(f"INFO :: Epoch: {epoch+1}")
i = 0
# For every batch in the dataset
for X_batch in dataset:
i=i+1
if i%100 == 0:
print(f"\tBatch number: {i} of {len(X_train_three)//BATCH_SIZE}")
#####################################
## TRAINING THE DISCRIMINATOR ######
###################################
# Create Noise
noise = tf.random.normal(shape=[BATCH_SIZE, INPUT_SHAPE])
# Generate numbers based just on noise input
gen_images = generator(noise)
# Concatenate Generated Images against the Real Ones
# TO use tf.concat, the data types must match!
X_fake_vs_real = tf.concat([gen_images, tf.dtypes.cast(X_batch,tf.float32)], axis=0)
# Targets set to zero for fake images and 1 for real images
y1 = tf.constant([[0.]] * BATCH_SIZE + [[1.]] * BATCH_SIZE)
# This gets rid of a Keras warning
discriminator.trainable = True
# Train the discriminator on this batch
discriminator.train_on_batch(X_fake_vs_real, y1)
#####################################
## TRAINING THE GENERATOR ######
###################################
# Create some noise
noise = tf.random.normal(shape=[BATCH_SIZE, INPUT_SHAPE])
# We want discriminator to belive that fake images are real
y2 = tf.constant([[1.]] * BATCH_SIZE)
# Avois a warning
discriminator.trainable = False
GAN.train_on_batch(noise, y2)
print("INFO :: Training Completed")
Making Predictions
The Generator expects a noise input tensor with input shape = INPUT_SHAPE. To have the Generator create an image - based on the previous training - we have to input such tensor of beautiful randomness.
# generate noise for 10 images
noise_input = tf.random.normal(shape=[10, INPUT_SHAPE])
print(noise_input.shape)
# (10, 100)
plt.imshow(noise_input)
generated_images = generator(noise_input)
generated_images.shape
# TensorShape([10, 28, 28])
# plot results
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
# ROW 1
plt.subplot(3, 3, 1)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(generated_images[0])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 2)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(generated_images[1])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 3)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(generated_images[2])
# ROW 2
plt.subplot(3, 3, 4)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(generated_images[3])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 5)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(generated_images[4])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 6)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(generated_images[5])
# ROW 3
plt.subplot(3, 3, 7)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(generated_images[6])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 8)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(generated_images[7])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 9)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(generated_images[8])
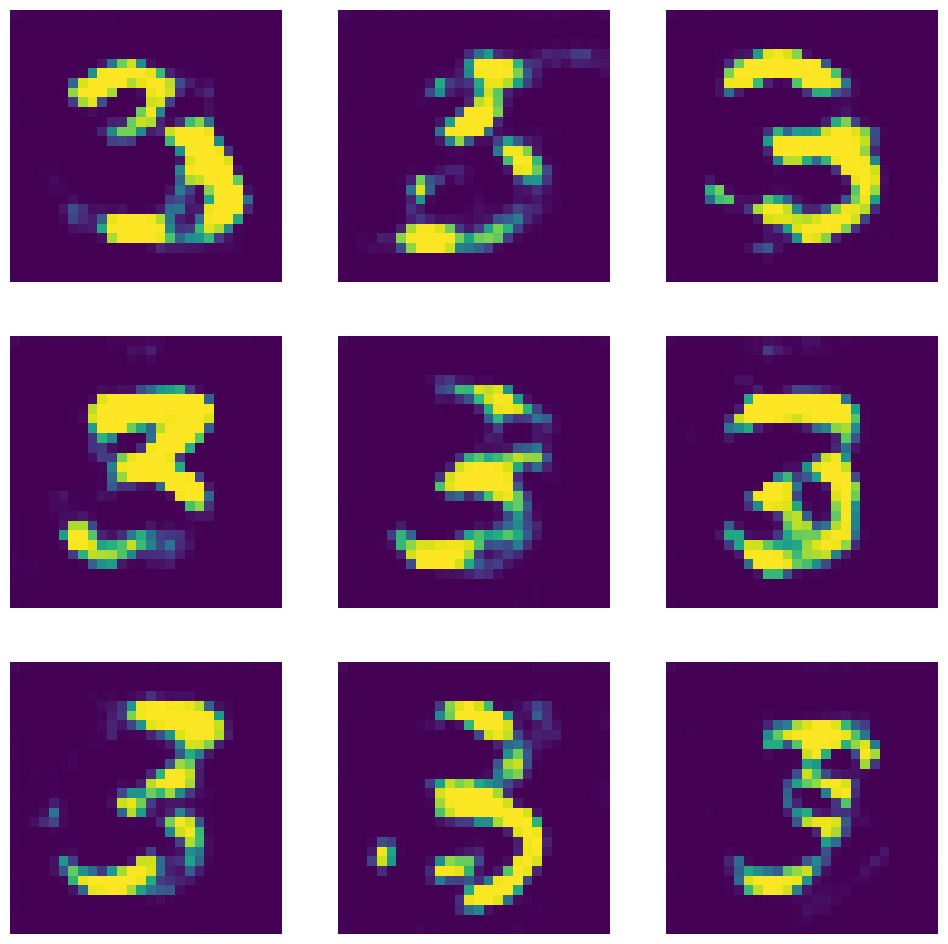
Why do all generated 3's look the same? => Combating Mode Collapse in GAN training: An Empirical Analysis using Hessian Eigenvalues
Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks (DCGAN)
A DCGAN is a direct extension of the GAN described above, except that it explicitly uses convolutional and convolutional-transpose layers in the discriminator and generator, respectively. It was first described by Radford et. al. in the paper Unsupervised Representation Learning With Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks.
The Discriminator is made up of strided convolution layers, batch norm layers, and LeakyReLU activations. The input is a 3x64x64 input image and the output is a scalar probability that the input is from the real data distribution.
The Generator is comprised of convolutional-transpose layers, batch norm layers, and ReLU activations. The input is a latent vector, (z), that is drawn from a standard normal distribution and the output is a 3x64x64 RGB image. The strided conv-transpose layers allow the latent vector to be transformed into a volume with the same shape as an image.
Dataset
# Generator will use tanh activation function for the last layer,
# so we want to reshape X_train to be within -1 to 1 limits
X_train_norm = X_train/255
X_train_reshaped = X_train_norm.reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1) * 2. - 1.
print(X_train_norm.shape, X_train_reshaped.shape, X_train_reshaped.min(), X_train_reshaped.max())
# only images with label `3`
X_train_three_dcgan = X_train_reshaped[y_train==3]
print(X_train_three_dcgan.shape)
# (6131, 28, 28, 1)
Create Batched Dataset
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(X_train_three_dcgan).shuffle(buffer_size=1000)
dataset = dataset.batch(BATCH_SIZE, drop_remainder=True).prefetch(1)
Building the Model
Generator
tf.random.set_seed(SEED)
generator = Sequential()
generator.add(Dense(7 * 7 * 128, input_shape=[INPUT_SHAPE]))
generator.add(Reshape([7, 7, 128]))
generator.add(BatchNormalization())
generator.add(Conv2DTranspose(64, kernel_size=5, strides=2, padding="same",
activation="relu"))
generator.add(BatchNormalization())
generator.add(Conv2DTranspose(1, kernel_size=5, strides=2, padding="same",
activation="tanh"))
Discriminator
discriminator = Sequential()
discriminator.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=5, strides=2, padding="same",
activation=LeakyReLU(0.3),
input_shape=[28, 28, 1]))
discriminator.add(Dropout(0.5))
discriminator.add(Conv2D(128, kernel_size=5, strides=2, padding="same",
activation=LeakyReLU(0.3)))
discriminator.add(Dropout(0.5))
discriminator.add(Flatten())
discriminator.add(Dense(1, activation="sigmoid"))
discriminator.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", optimizer="adam")
discriminator.trainable = False
GAN = Sequential([generator, discriminator])
GAN.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", optimizer="adam")
GAN.summary()
# Model: "sequential_4"
# _________________________________________________________________
# Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
# =================================================================
# sequential_1 (Sequential) (None, 28, 28, 1) 840705
# sequential_3 (Sequential) (None, 1) 212865
# =================================================================
# Total params: 1,053,570
# Trainable params: 840,321
# Non-trainable params: 213,249
# _________________________________________________________________
Model Training
# Grab the seprate components
generator, discriminator = GAN.layers
# For every epcoh
for epoch in range(EPOCHS):
print(f"INFO :: Epoch: {epoch+1}")
i = 0
# For every batch in the dataset
for X_batch in dataset:
i=i+1
if i%20 == 0:
print(f"\tBatch number: {i} of {len(X_train_three)//BATCH_SIZE}")
#####################################
## TRAINING THE DISCRIMINATOR ######
###################################
# Create Noise
noise = tf.random.normal(shape=[BATCH_SIZE, INPUT_SHAPE])
# Generate numbers based just on noise input
gen_images = generator(noise)
# Concatenate Generated Images against the Real Ones
# TO use tf.concat, the data types must match!
X_fake_vs_real = tf.concat([gen_images, tf.dtypes.cast(X_batch,tf.float32)], axis=0)
# Targets set to zero for fake images and 1 for real images
y1 = tf.constant([[0.]] * BATCH_SIZE + [[1.]] * BATCH_SIZE)
# This gets rid of a Keras warning
discriminator.trainable = True
# Train the discriminator on this batch
discriminator.train_on_batch(X_fake_vs_real, y1)
#####################################
## TRAINING THE GENERATOR ######
###################################
# Create some noise
noise = tf.random.normal(shape=[BATCH_SIZE, INPUT_SHAPE])
# We want discriminator to belive that fake images are real
y2 = tf.constant([[1.]] * BATCH_SIZE)
# Avois a warning
discriminator.trainable = False
GAN.train_on_batch(noise, y2)
print("TRAINING COMPLETE")
Making Predictions
The Generator expects a noise input tensor with input shape = INPUT_SHAPE. To have the Generator create an image - based on the previous training - we have to input such tensor of beautiful randomness.
# generate noise for 10 images
noise_input = tf.random.normal(shape=[10, INPUT_SHAPE])
print(noise_input.shape)
# (10, 100)
generated_images = generator(noise_input)
generated_images.shape
# TensorShape([10, 28, 28])
# plot results
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
# ROW 1
plt.subplot(3, 3, 1)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(generated_images[0])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 2)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(generated_images[1])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 3)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(generated_images[2])
# ROW 2
plt.subplot(3, 3, 4)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(generated_images[3])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 5)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(generated_images[4])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 6)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(generated_images[5])
# ROW 3
plt.subplot(3, 3, 7)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(generated_images[6])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 8)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(generated_images[7])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 9)
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(generated_images[8])