YOLOv7 Label Conversion

In the previous step we cloned the YOLOv7 repository and run predictions using testing weights. I then trained YOLOv7 with a custom dataset that was pre-labeled the "YOLO Way".
Another annotations format that can be generated by LabelImg is the PASCAL VOC format. I now want to see how to transfer a dataset that was labeled that way into a YOLO training workflow. I am going to use the following Kaggle dataset:
And for the transfer code had help from Convert PASCAL VOC XML to YOLO for Object Detection by Ng Wai Foong.
Getting YOLOv7
Training Weights
I already went through all the steps to download and test-run YOLOv7. I ran into difficulties with my graphic card only having 6Gig of VRAM (Nvidia GTX 1060) which forced me to reduce the batch size to 1. Since this freed up a lot of memory - a size of 2 was too much, while 1 underutilized the card - I want to use the following weights:
wget https://github.com/WongKinYiu/yolov7/releases/download/v0.1/yolov7-e6e_training.pt
The e6e increases the amounts of parameter from ~ 40Mio to ~ 150Mio... let's see what happens...
Configuration
Now we need to configure YOLO. First create a copy of the following file and call it something like:
cp yolov7/cfg/training/yolov7-e6e.yaml yolov7/cfg/training/yolov7-e6e-ppe.yaml
Here we only need to adjust the amount of classes we expect in our dataset - 3:
# parameters
nc: 3 # number of classes
Error: I am getting an
IndexError: list index out of rangewhen trying to useyolov7-e6e.yamlfile. When I switch toyolov7-custom.yamlthe training works. Even though I am using thee6eweights:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "yolov7/train.py", line 616, in <module>
train(hyp, opt, device, tb_writer)
File "yolov7/train.py", line 363, in train
loss, loss_items = compute_loss_ota(pred, targets.to(device), imgs) # loss scaled by batch_size
File "yolov7/utils/loss.py", line 585, in __call__
bs, as_, gjs, gis, targets, anchors = self.build_targets(p, targets, imgs)
File "yolov7/utils/loss.py", line 677, in build_targets
b, a, gj, gi = indices[i]
IndexError: list index out of range
UPDATE: Apparently you need to use train_aux.py instead of train.py to work with
e6eweights. I will test this next.
Next create the directories yolov7/custom_data/ppe and add a data file ppe-data.yml:
train: ./custom_data/ppe/train
val: ./custom_data/ppe/validation
test: ./custom_data/ppe/test
# Classes
nc: 3 # number of classes
names: ['with_mask', 'without_mask', 'mask_worn_incorrect']
The original class was
mask_weared_incorrect- I searched and replaced it tomask_worn_incorrect
Preparing the Dataset
This dataset contains 853 images belonging to the 3 classes, as well as their bounding boxes in the PASCAL VOC format. The classes are:
With maskWithout maskMask worn incorrectly
The annotations are in an XML format:
<annotation>
<folder>images</folder>
<filename>maksssksksss852.png</filename>
<size>
<width>267</width>
<height>400</height>
<depth>3</depth>
</size>
<segmented>0</segmented>
<object>
<name>with_mask</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<occluded>0</occluded>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>139</xmin>
<ymin>94</ymin>
<xmax>198</xmax>
<ymax>147</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
</annotation>
The downloaded dataset is only split into images and annotations:
yolov7/custom_data
└── ppe
├── ppe-data.yml
├── images
└── annotations
We now need to convert the annotation-data format from PASCAL VOC to YOLO and split the data into train, val, test-folders:
yolov7/convert_xml_to_yolo.py
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import seaborn as sns
import os
import shutil
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import glob
import json
# Function for conversion XML to YOLO
# based on https://towardsdatascience.com/convert-pascal-voc-xml-to-yolo-for-object-detection-f969811ccba5
def xml_to_yolo_bbox(bbox, w, h):
# xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax
x_center = ((bbox[2] + bbox[0]) / 2) / w
y_center = ((bbox[3] + bbox[1]) / 2) / h
width = (bbox[2] - bbox[0]) / w
height = (bbox[3] - bbox[1]) / h
return [x_center, y_center, width, height]
# create folders
def create_folder(path):
if not os.path.exists(path):
os.makedirs(path)
print("INFO :: Path '%s' created" %path)
create_folder('custom_data/ppe/train/images')
create_folder('custom_data/ppe/train/labels')
create_folder('custom_data/ppe/validation/images')
create_folder('custom_data/ppe/validation/labels')
create_folder('custom_data/ppe/test/images')
create_folder('custom_data/ppe/test/labels')
# get all source files
img_src_folder = 'custom_data/ppe/images'
label_src_folder = 'custom_data/ppe/annotations'
_, _, files = next(os.walk(img_src_folder))
pos = 0
for f in files:
source_img = os.path.join(img_src_folder, f)
if pos < 700:
dest_folder = 'custom_data/ppe/train'
elif (pos >= 700 and pos < 800):
dest_folder = 'custom_data/ppe/validation'
else:
dest_folder = 'custom_data/ppe/test'
destination_img = os.path.join(dest_folder,'images', f)
shutil.copy(source_img, destination_img)
# check for corresponding label
label_file_basename = os.path.splitext(f)[0]
label_source_file = f"{label_file_basename}.xml"
label_dest_file = f"{label_file_basename}.txt"
label_source_path = os.path.join(label_src_folder, label_source_file)
label_dest_path = os.path.join(dest_folder, 'labels', label_dest_file)
# if file exists, copy it to target folder
if os.path.exists(label_source_path):
# parse the content of the xml file
tree = ET.parse(label_source_path)
root = tree.getroot()
width = int(root.find("size").find("width").text)
height = int(root.find("size").find("height").text)
classes = ['with_mask', 'without_mask', 'mask_worn_incorrect']
result = []
for obj in root.findall('object'):
label = obj.find("name").text
# check for new classes and append to list
index = classes.index(label)
pil_bbox = [int(x.text) for x in obj.find("bndbox")]
yolo_bbox = xml_to_yolo_bbox(pil_bbox, width, height)
# convert data to string
bbox_string = " ".join([str(x) for x in yolo_bbox])
result.append(f"{index} {bbox_string}")
if result:
# generate a YOLO format text file for each xml file
with open(label_dest_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write("\n".join(result))
pos += 1
Make sure that all the paths in here match your dir structure - also replace the / with \\ in path variables if your are on Windows. And run the script:
python convert_xml_to_yolo.py
INFO :: Path 'custom_data/ppe/train/images' created
INFO :: Path 'custom_data/ppe/train/labels' created
INFO :: Path 'custom_data/ppe/validation/images' created
INFO :: Path 'custom_data/ppe/validation/labels' created
INFO :: Path 'custom_data/ppe/test/images' created
INFO :: Path 'custom_data/ppe/test/labels' created
Check the custom_data folder - you should now have a split all the data into the three training, testing and validating directories:
yolov7/custom_data
└── ppe
├── ppe-data.yml
├── test
│ ├── images
│ │ └── 53 items
│ └── labels
│ └── 53 items
├── train
│ ├── images
│ │ └── 700 items
│ └── labels
│ │ └── 700 items
└── validation
├── images
│ └── 100 items
└── labels
└── 100 items
And all the labels are now in the expected YOLO format:
0 0.2425 0.36099585062240663 0.115 0.2074688796680498
Model Fitting
The data is now compatible with YOLOv7 and can be used to train a model to recognize personal protection equipment for us:
python train.py --epochs 100 --weights weights/yolov7-e6e_training.pt --data custom_data/ppe/ppe-data.yml --workers 4 --batch-size 1 --img 416 --cfg cfg/training/yolov7_custom.yaml --name yolov7-ppe
The run took around 4hrs with the following - disappointing - results:
Epoch gpu_mem box obj cls total
99/99 2.67G 0.02546 0.01013 0.003265 0.03886
Class Images Labels P R
all 100 442 0.399 0.372
with_mask 100 368 0.765 0.802
without_mask 100 60 0.431 0.315
mask_worn_incorrect 100 14 0 0
100 epochs completed in 3.783 hours.
Optimizer stripped from runs/train/yolov7-ppe4/weights/last.pt, 74.8MB
Optimizer stripped from runs/train/yolov7-ppe4/weights/best.pt, 74.8MB
Testing
python test.py --weights runs/train/yolov7-ppe4/weights/best.pt \
--task test \
--data custom_data/ppe/ppe-data.yml
Class Images Labels P R
all 53 223 0.357 0.476
with_mask 53 191 0.676 0.749
without_mask 53 25 0.395 0.679
mask_worn_incorrect 53 7 0 0
Speed: 56.5/1.1/57.6 ms inference/NMS/total per 640x640 image at batch-size 32
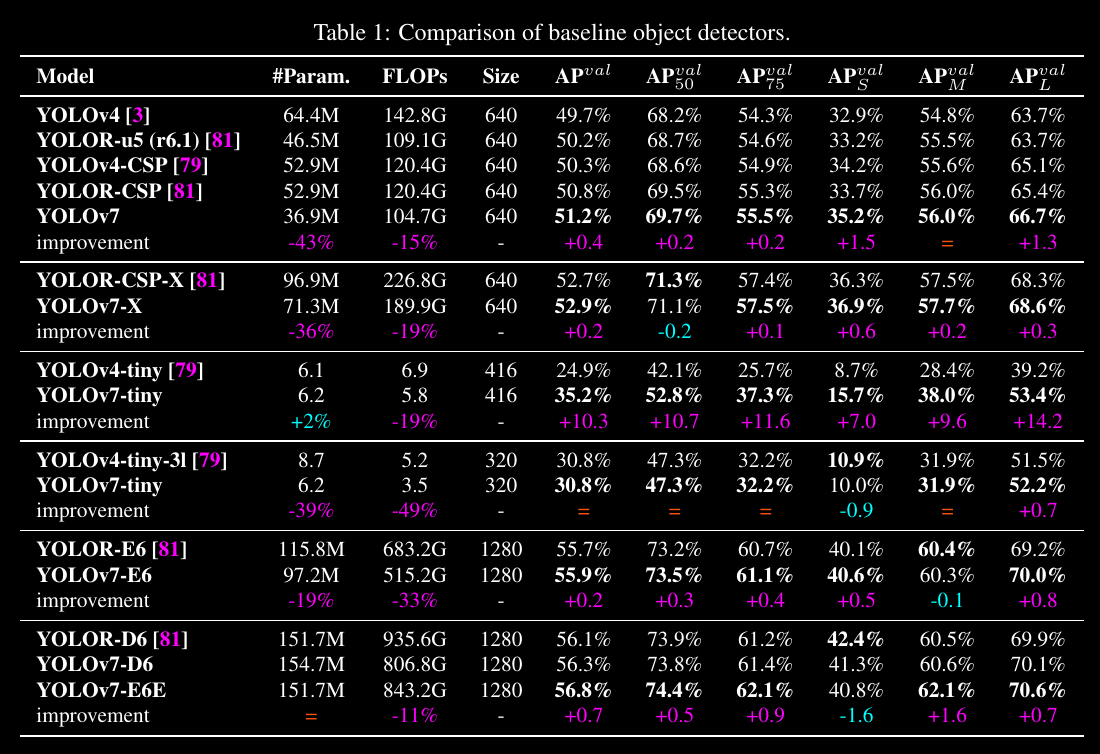
Just terrible...
Correction
python train_aux.py --device 0 --epochs 20 --weights weights/yolov7-e6e_training.pt --data custom_data/ppe/ppe-data.yml --workers 4 --batch-size 1 --img 416 --cfg cfg/training/yolov7-e6e-ppe.yaml --name yolov7-aux-ppe
Here I am getting the following error message:
RuntimeError: indices should be either on cpu or on the same device as the indexed tensor (cpu)
Hmm there are several proposed solutions: Github Issue, Stack Overflow. But none of the appear to be working for me right now. So let's drop the e6e and try the regular YOLOv4 model:
python train.py --epochs 20 --weights weights/yolov7_training.pt --data custom_data/ppe/ppe-data.yml --workers 4 --batch-size 1 --img 640 640 --cfg cfg/training/yolov7_custom.yaml --name yolov7-regular-ppe
And this looks more promising - already after 20 epochs:
Class Images Labels P R
all 100 442 0.942 0.127
with_mask 100 368 0.827 0.38
without_mask 100 60 1 0
mask_worn_incorrect 100 14 1 0
20 epochs completed in 1.116 hours.
Optimizer stripped from runs/train/yolov7-regular-ppe/weights/last.pt, 74.8MB
Optimizer stripped from runs/train/yolov7-regular-ppe/weights/best.pt, 74.8MB
Testing
python test.py --weights runs/train/yolov7-regular-ppe/weights/best.pt \
--task test \
--data custom_data/ppe/ppe-data.yml
Class Images Labels P R
all 53 223 0.935 0.166
with_mask 53 191 0.805 0.497
without_mask 53 25 1 0
mask_worn_incorrect 53 7 1 0
Prediction
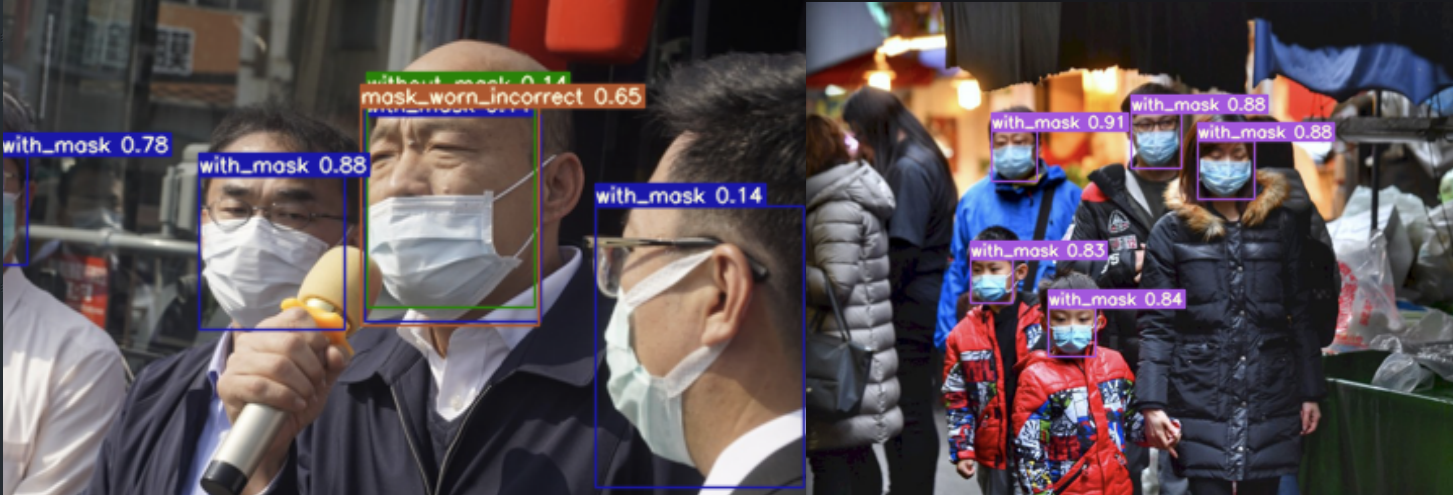
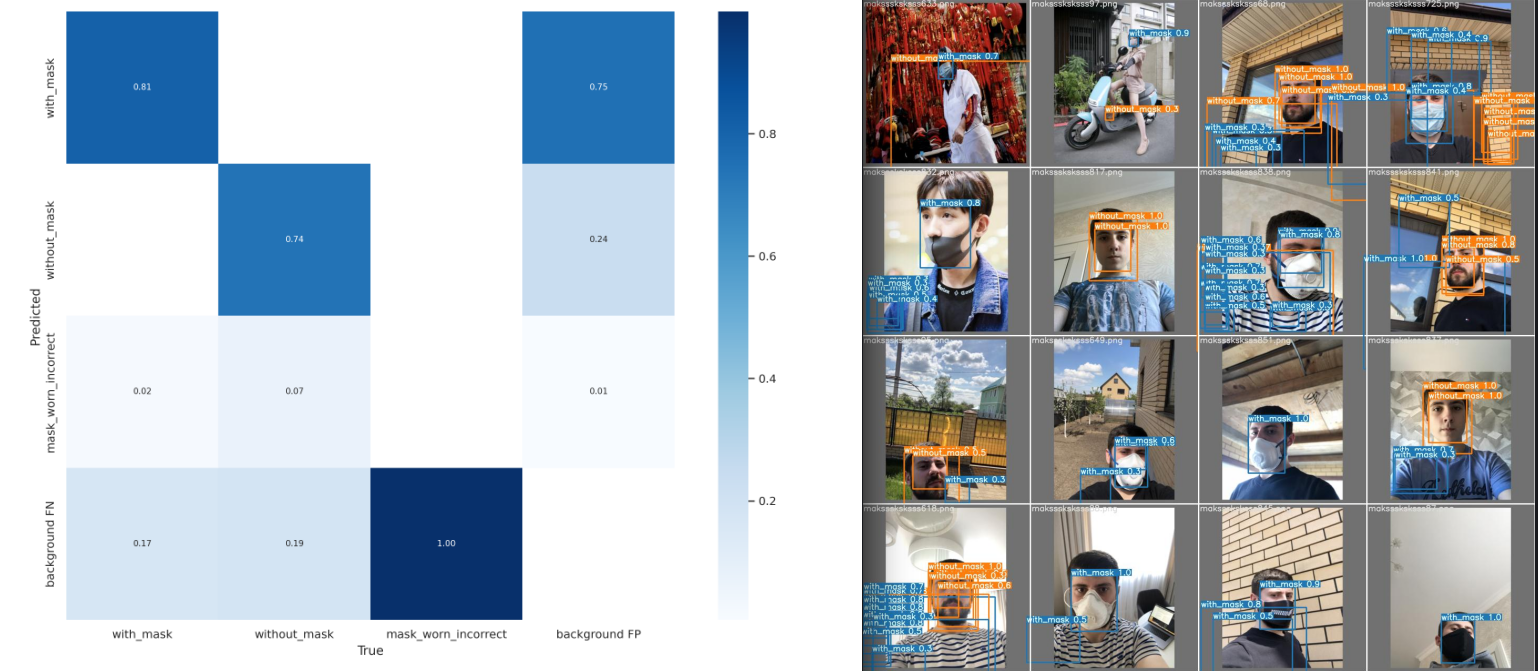
The prediction works "best" for frontal shots of large groups of people. But there are a lot of false positives. The model fails completely when dealing with close-ups:
python detect.py --weights runs/train/yolov7-regular-ppe/weights/best.pt \
--conf 0.1 \
--img-size 640 \
--source custom_data/ppe/test/images/maksssksksss836.png

But it is far from great yet - the model has about a 50:50 chance to detect a mask. And zero chance to detect no mask or a wrongly worn mask. The next step is to extend the the training and see if the R-value improves over time.
Extended Run
Night-shift run... yolov7x_training.pt
I decided to give YOLOv7x a try. It is much more complex compared to YOLOv7 (36.9M vs 71.3M parameter). And - to my knowledge - it does not require you to use train_aux.py that was causing the issues earlier. So all I needed was to download the matching training weights and create a copy of cfg/training/yolov7x.yaml with the correct number of classes:
python train.py --device 0 --epochs 200 --weights weights/yolov7x_training.pt --data custom_data/ppe/ppe-data.yml --workers 4 --batch-size 1 --img 640 640 --cfg cfg/training/yolov7x-ppe.yaml --name yolov7x-ppe
The run over 200 Epochs took my machine 14.5hrs and ended with the following results:
199/199 3.34G 0.01889 0.008947 0.001511 0.02935
Class Images Labels P R
all 100 442 0.135 0.744
with_mask 100 368 0.104 0.902
without_mask 100 60 0.211 0.617
mask_worn_incorrect 100 14 0.0908 0.714
200 epochs completed in 14.672 hours.
Optimizer stripped from runs/train/yolov7x-ppe/weights/last.pt, 142.1MB
Optimizer stripped from runs/train/yolov7x-ppe/weights/best.pt, 142.1MB
Testing
python test.py --weights runs/train/yolov7x-ppe/weights/best.pt \
--task test \
--data custom_data/ppe/ppe-data.yml
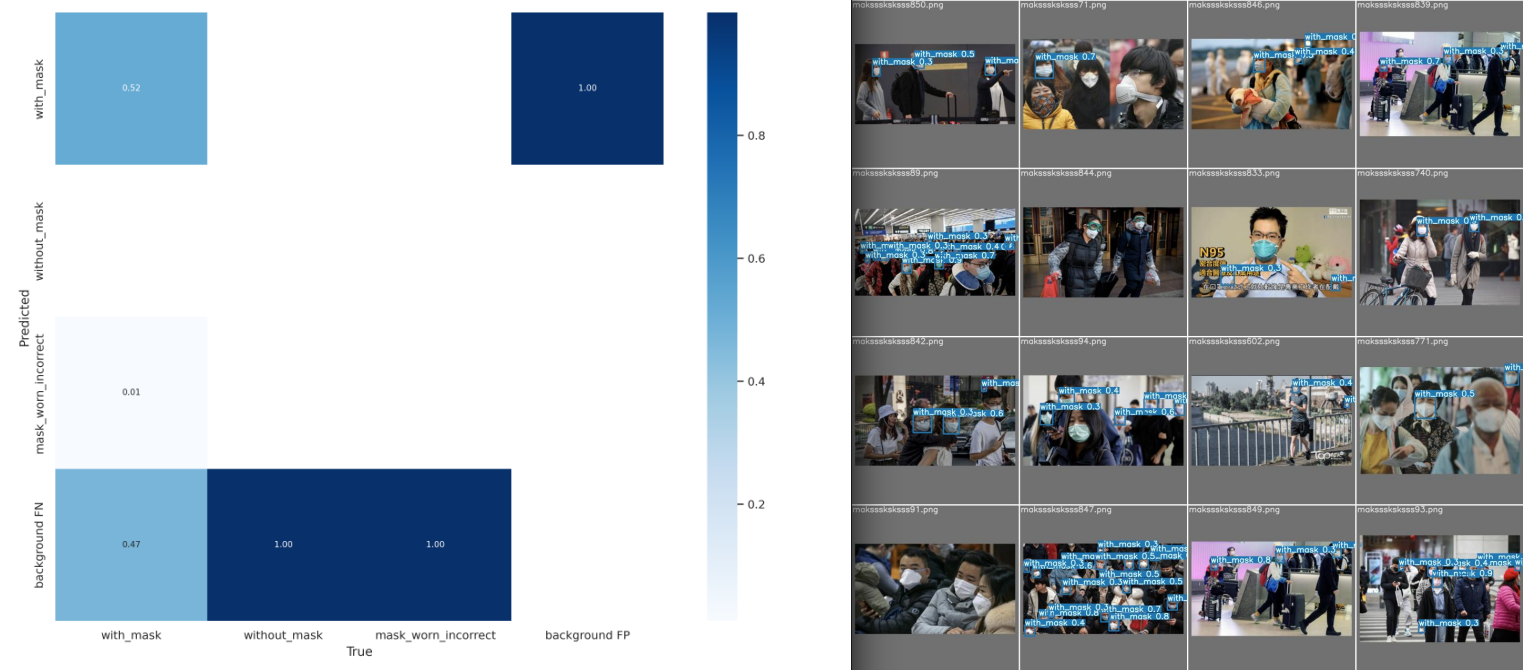
Class Images Labels P R
all 53 223 0.978 0.712
with_mask 53 191 0.935 0.77
without_mask 53 25 1 0.8
mask_worn_incorrect 53 7 1 0.566
Speed: 81.4/0.8/82.2 ms inference/NMS/total per 640x640 image at batch-size 32
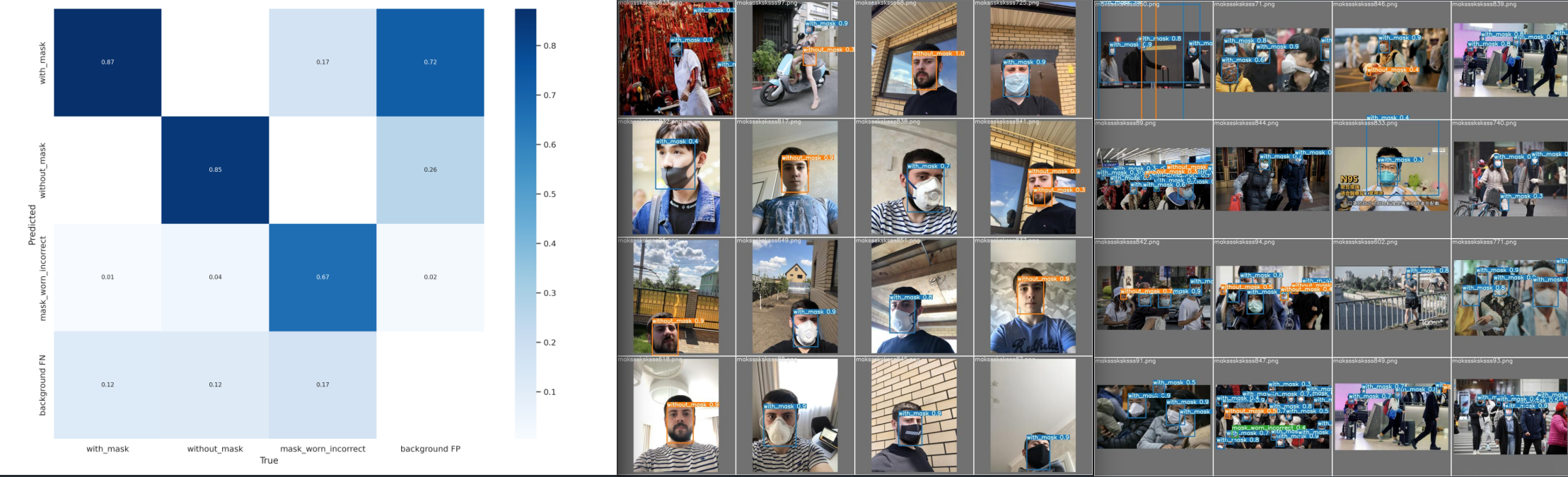
The confusion matrix correlates nicely with the test predictions. 87% of masks were identified correctly. For faces without masks we get 85%. For incorrectly worn masks - a much more complicated case - we are already at 67%. But the model is still seeing a lot of masks in the background that do not exist. But overall - a successful training 👍
Predictions
For a comparison I want to run the same predictions I used with the previous model - maksssksksss836.png and maksssksksss99.png:
python detect.py --weights runs/train/yolov7x-ppe/weights/best.pt \
--conf 0.5 \
--img-size 640 \
--source custom_data/ppe/test/images/maksssksksss836.png
For the close-up image I decreased the confidence barrier to 0.1 to see if the person on the right would show up with the mask in a side-profile. And he does - it is really impressive:
