- Tensorflow Unsupervised Learning
See also:
- Fun, fun, tensors: Tensor Constants, Variables and Attributes, Tensor Indexing, Expanding and Manipulations, Matrix multiplications, Squeeze, One-hot and Numpy
- Tensorflow 2 - Neural Network Regression: Building a Regression Model, Model Evaluation, Model Optimization, Working with a "Real" Dataset, Feature Scaling
- Tensorflow 2 - Neural Network Classification: Non-linear Data and Activation Functions, Model Evaluation and Performance Improvement, Multiclass Classification Problems
- Tensorflow 2 - Convolutional Neural Networks: Binary Image Classification, Multiclass Image Classification
- Tensorflow 2 - Transfer Learning: Feature Extraction, Fine-Tuning, Scaling
- Tensorflow 2 - Unsupervised Learning: Autoencoder Feature Detection, Autoencoder Super-Resolution, Generative Adverserial Networks
Tensorflow Unsupervised Learning
Principle of Dimensionality Reduction
Using Autoencoders to remove "noisy dimensions" in our dataset to be able to extract hidden features.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten, Reshape, GaussianNoise
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import SGD, Adam
# global variables
SEED = 42
# create random feature blobs
data = make_blobs(n_samples=300,
n_features=2,
centers=2,
cluster_std=1.0,
random_state=SEED)
X, y = data
# create random dataset
np.random.seed(seed=SEED)
z_noise = np.random.normal(size=len(X))
z_noise = pd.Series(z_noise)
# combine data into single dataframe
features = pd.DataFrame(X)
features = pd.concat([features,z_noise], axis=1)
features.columns = ['X1', 'X2', 'Xnoise']
# this generated a dataframe with 3 colums for our data:
print(features.head())
| X1 | X2 | Xnoise | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -7.338988 | -7.729954 | 0.496714 |
| 1 | -7.740041 | -7.264665 | -0.138264 |
| 2 | -1.686653 | 7.793442 | 0.647689 |
| 3 | 4.422198 | 3.071947 | 1.523030 |
| 4 | -8.917752 | -7.888196 | -0.234153 |
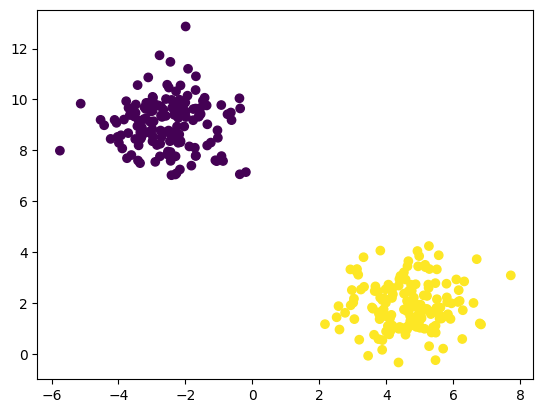
# plotting Y=f(x) shows 2 distinct features
plt.scatter(features['X1'], features['X2'], c=y)
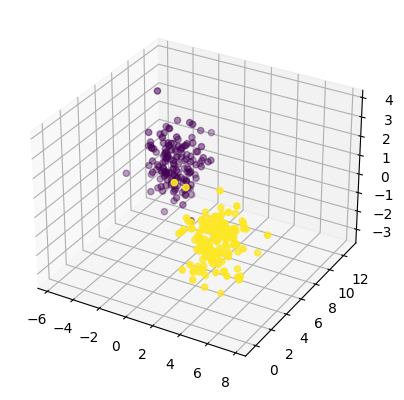
# add a third dimension from the noise data
# this noisy dimension(s) are supposed to
# make it more difficult to see the underlying
# 2 features
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.scatter(features['X1'], features['X2'], features['Xnoise'], c=y)
# normalize the dataset
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
scaled_data = scaler.fit_transform(features)
# this generated a dataframe with 3 colums for our data:
print(scaled_data[:5])
array([[0.123409 , 0.0694226 , 0.52692164],
[0.09881332, 0.09166767, 0.4374124 ],
[0.4700545 , 0.81158342, 0.54820363],
[0.84469708, 0.58585258, 0.67159543],
[0.02658684, 0.06185718, 0.42389547]])
Build the Autoencoder
# build an encoder that reduces dimensionality from 3 => 2
encoder = Sequential([
Dense(units=2, activation='relu', input_shape=[3])
])
# and an encoder that brings it back up from 2 => 3
decoder = Sequential([
Dense(units=3, activation='relu', input_shape=[2])
])
# compile both layers into the autoencoder model
autoencoder = Sequential([encoder, decoder])
autoencoder.compile(loss='mse', optimizer=SGD(learning_rate=1.5))
Train the Autoencoder
autoencoder.fit(scaled_data, scaled_data, epochs=5)
# The encoder now reduces the dimensions of our dataset to 2
# when we run predictions from the encoder we will get
# 2-dimensional results that should have stripped the
# noisy 3rd dimension we added
encoded_2dim = encoder.predict(scaled_data)
# (300, 2) <= (300, 3)
print(encoded_2dim.shape, scaled_data.shape)
encoded_2dim
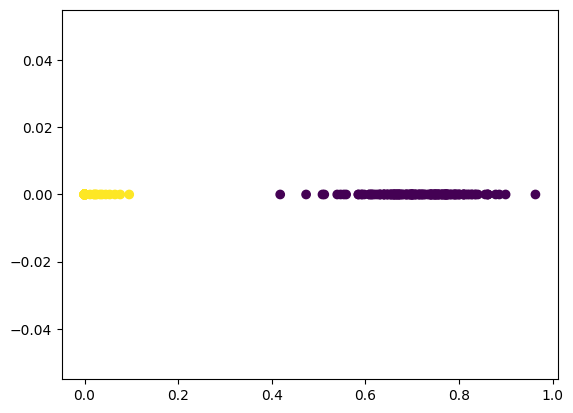
Visualize the Results
plt.scatter(encoded_2dim[:,0], encoded_2dim[:,1], c=y)
# the encoder simplified our dataset and extracted 2 clearly
# defined features that might have been obfuscated by the
# extra dimensions in our dataset
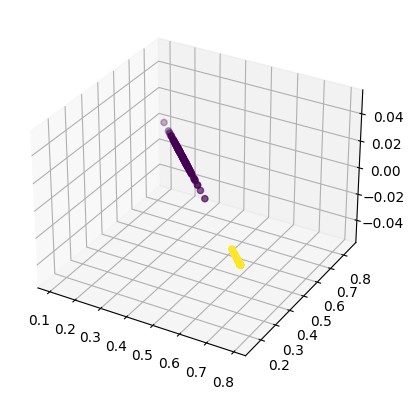
decoded_2to3dim = autoencoder.predict(scaled_data)
print(decoded_2to3dim.shape, scaled_data.shape)
# (300, 3) <= (300, 2) <= (300, 3)
decoded_2to3dim
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.scatter(decoded_2to3dim[:,0], decoded_2to3dim[:,1], decoded_2to3dim[:,2], c=y)
Autoencoders for Image Data
Create a noisy version of the MNIST digits dataset and train an autoencoder to generate de-noised images from this source.
(X_train, y_train), (X_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
plt.imshow(X_train[88])
# normalize images
X_train = X_train/255
X_test = X_test/255
Building the Autoencoder
The dataset starts out with 28*28 px images = 784 dimensions. The Encoder should now, several times over several layers, approx. cut this number in half until a minimum of dimensions is reached in a hidden layer.
The following Decoder should then take those reduced feature maps and reconstruct the original image from it. By validating the against the original, not noisy images we should be able to train the Autoencoder to denoise images.
Let's get started by an autoencoder that can read the original image, reduces it to ~3% and then reconstruct the original image from this state:
encoder = Sequential([
# generate (28, 28) => (784) shape
Flatten(input_shape=[28, 28], name='input_layer'),
# cut dimensions in half
Dense(units=392, activation='relu', name="reducer50"),
# cut dimensions in half
Dense(units=196, activation='relu', name="reducer25"),
# cut dimensions in half
Dense(units=98, activation='relu', name="reducer12"),
# cut dimensions in half
Dense(units=49, activation='relu', name="reducer6"),
# cut dimensions in ~ half
Dense(units=24, activation='relu', name='hidden_layer')
])
decoder = Sequential([
Dense(units=49, activation='relu', input_shape=[24], name='expander6'),
Dense(units=98, activation='relu', name='expander12'),
Dense(units=98, activation='relu', name='expander25'),
Dense(units=392, activation='relu', name='expander50'),
Dense(units=784, activation='sigmoid', name='expander100'),
Reshape([28, 28], name='output_layer')
])
autoencoder = Sequential([encoder, decoder])
autoencoder.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
# optimizer=SGD(learning_rate=1.5),
optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=1e-3),
metrics=['accuracy'])
tf.random.set_seed(SEED)
# fit the autoencoder to training dataset
autoencoder.fit(X_train, X_train, epochs=25,
validation_data=[X_test, X_test])
# Epoch 25/25
# 6s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0898 - accuracy: 0.3063 - val_loss: 0.0923 - val_accuracy: 0.2968
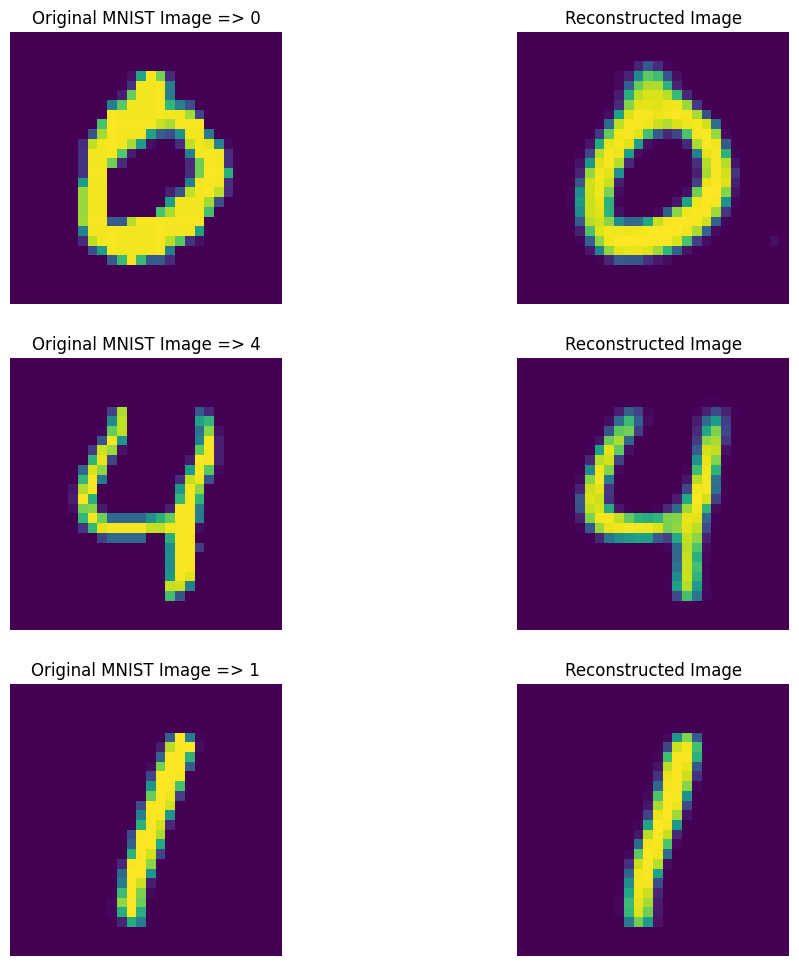
Run Predictions
# get 10 sample predictions from testing dataset
passed_images = autoencoder.predict(X_test[:10])
# select 3 images out of 10 samples
n = [3, 4, 5]
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
# ROW 1
plt.subplot(3, 2, 1)
plt.title(f"Original MNIST Image => {y_test[n[0]]}")
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(X_test[n[0]])
plt.subplot(3, 2, 2)
plt.title("Reconstructed Image")
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(passed_images[n[0]])
# ROW 2
plt.subplot(3, 2, 3)
plt.title(f"Original MNIST Image => {y_test[n[1]]}")
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(X_test[n[1]])
plt.subplot(3, 2, 4)
plt.title("Reconstructed Image")
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(passed_images[n[1]])
# ROW 3
plt.subplot(3, 2, 5)
plt.title(f"Original MNIST Image => {y_test[n[2]]}")
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(X_test[n[2]])
plt.subplot(3, 2, 6)
plt.title("Reconstructed Image")
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(passed_images[n[2]])
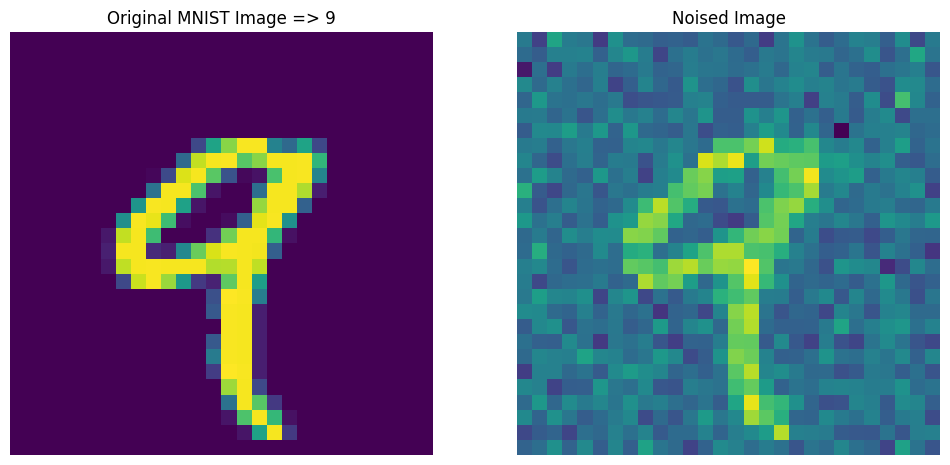
Autoencoders for Noise Removal
# generating noise
sample = GaussianNoise(0.2)
noisy = sample(X_train[:10], training=True)
n = 4
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
# ROW 1
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.title(f"Original MNIST Image => {y_train[n]}")
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(X_train[n])
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.title("Noised Image")
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(noisy[n])
Build the Denoise Autoencoder
tf.random.set_seed(SEED)
encoder = Sequential([
# generate (28, 28) => (784) shape
Flatten(input_shape=[28, 28], name='input_layer'),
# add noise to source image
GaussianNoise(0.2),
# cut dimensions in half
Dense(units=392, activation='relu', name="reducer50"),
# cut dimensions in half
Dense(units=196, activation='relu', name="reducer25"),
# cut dimensions in half
Dense(units=98, activation='relu', name="reducer12"),
# cut dimensions in half
Dense(units=49, activation='relu', name="reducer6"),
# cut dimensions in ~ half
Dense(units=24, activation='relu', name='hidden_layer')
])
decoder = Sequential([
Dense(units=49, activation='relu', input_shape=[24], name='expander6'),
Dense(units=98, activation='relu', name='expander12'),
Dense(units=98, activation='relu', name='expander25'),
Dense(units=392, activation='relu', name='expander50'),
Dense(units=784, activation='sigmoid', name='expander100'),
Reshape([28, 28], name='output_layer')
])
noise_remover = Sequential([encoder, decoder])
noise_remover.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=1e-3),
metrics=['accuracy'])
noise_remover.fit(X_train, X_train, epochs=25,
validation_data=[X_test, X_test])
# Epoch 25/25
# 6s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0946 - accuracy: 0.2949 - val_loss: 0.0913 - val_accuracy: 0.2986
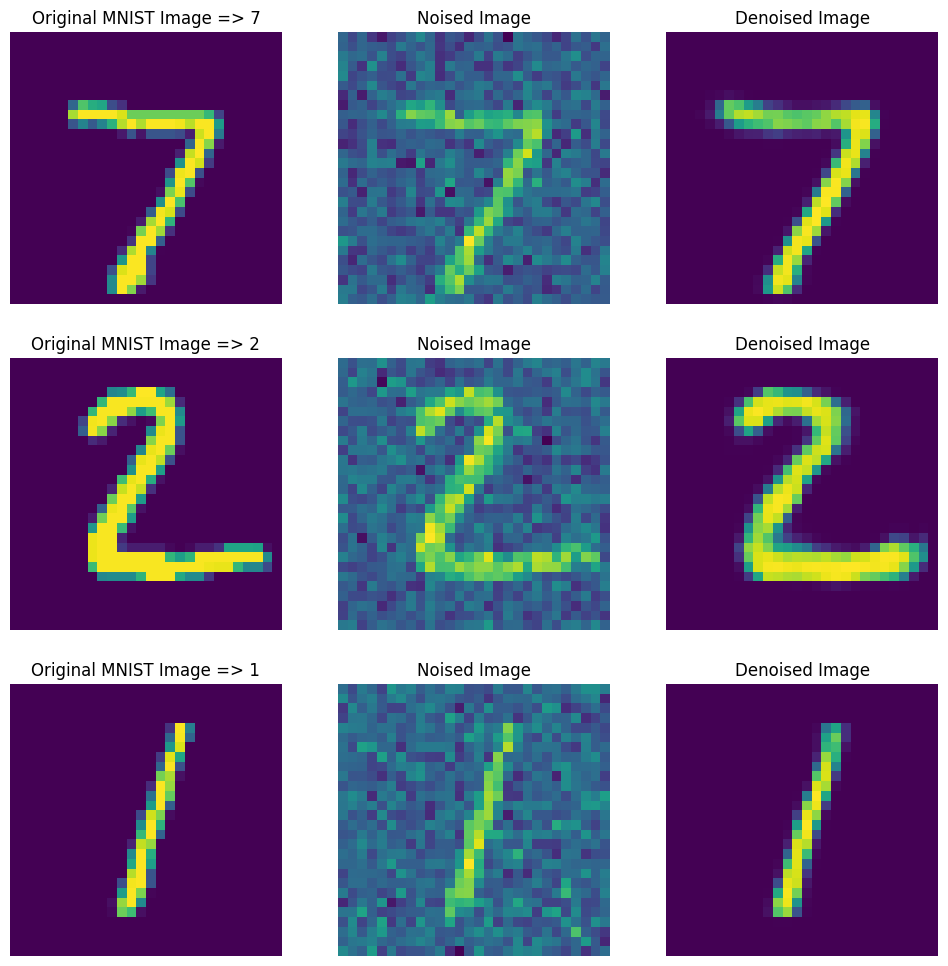
Run Denoiser
noisy_samples = sample(X_test[:3], training=True)
denoised_samples = noise_remover(noisy_samples)
# plot results
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
# ROW 1
plt.subplot(3, 3, 1)
plt.title(f"Original MNIST Image => {y_test[0]}")
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(X_test[0])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 2)
plt.title("Noised Image")
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(noisy_samples[0])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 3)
plt.title("Denoised Image")
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(denoised_samples[0])
# ROW 2
plt.subplot(3, 3, 4)
plt.title(f"Original MNIST Image => {y_test[1]}")
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(X_test[1])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 5)
plt.title("Noised Image")
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(noisy_samples[1])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 6)
plt.title("Denoised Image")
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(denoised_samples[1])
# ROW 3
plt.subplot(3, 3, 7)
plt.title(f"Original MNIST Image => {y_test[2]}")
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(X_test[2])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 8)
plt.title("Noised Image")
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(noisy_samples[2])
plt.subplot(3, 3, 9)
plt.title("Denoised Image")
plt.axis(False)
plt.imshow(denoised_samples[2])
Food
Variations in preference for different food types in the UK
wget https://github.com/emtrujillo-lab/bggn213/blob/3fdf3e1f373545a420de9fb45a2a8e68ee5478fa/Class09/Class9/UK_foods.csv
Prepare the Dataset
df = pd.read_csv('./UK_foods.csv', index_col='Unnamed: 0')
df
| England | Wales | Scotland | N.Ireland | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cheese | 105 | 103 | 103 | 66 |
| Carcass_meat | 245 | 227 | 242 | 267 |
| Other_meat | 685 | 803 | 750 | 586 |
| Fish | 147 | 160 | 122 | 93 |
| Fats_and_oils | 193 | 235 | 184 | 209 |
| Sugars | 156 | 175 | 147 | 139 |
| Fresh_potatoes | 720 | 874 | 566 | 1033 |
| Fresh_Veg | 253 | 265 | 171 | 143 |
| Other_Veg | 488 | 570 | 418 | 355 |
| Processed_potatoes | 198 | 203 | 220 | 187 |
| Processed_Veg | 360 | 365 | 337 | 334 |
| Fresh_fruit | 1102 | 1137 | 957 | 674 |
| Cereals | 1472 | 1582 | 1462 | 1494 |
| Beverages | 57 | 73 | 53 | 47 |
| Soft_drinks | 1374 | 1256 | 1572 | 1506 |
| Alcoholic_drinks | 375 | 475 | 458 | 135 |
| Confectionery | 54 | 64 | 62 | 41 |
# create a heatmap with pandas
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.pcolor(df)
plt.yticks(np.arange(0.5, len(df.index), 1), df.index)
plt.xticks(np.arange(0.5, len(df.columns), 1), df.columns)
plt.xticks(rotation=70, fontsize=12)
plt.yticks(fontsize=12)
plt.show()
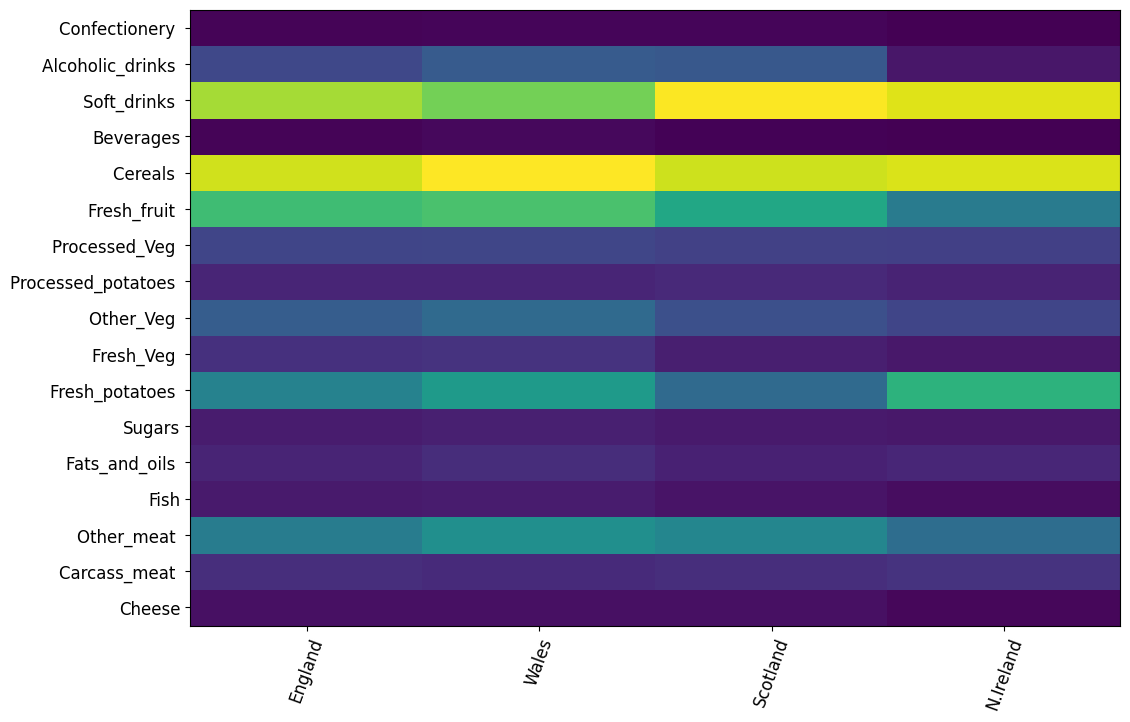
df_t = df.transpose()
df_t
| Cheese | Carcass_meat | Other_meat | Fish | Fats_and_oils | Sugars | Fresh_potatoes | Fresh_Veg | Other_Veg | Processed_potatoes | Processed_Veg | Fresh_fruit | Cereals | Beverages | Soft_drinks | Alcoholic_drinks | Confectionery | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| England | 105 | 245 | 685 | 147 | 193 | 156 | 720 | 253 | 488 | 198 | 360 | 1102 | 1472 | 57 | 1374 | 375 | 54 |
| Wales | 103 | 227 | 803 | 160 | 235 | 175 | 874 | 265 | 570 | 203 | 365 | 1137 | 1582 | 73 | 1256 | 475 | 64 |
| Scotland | 103 | 242 | 750 | 122 | 184 | 147 | 566 | 171 | 418 | 220 | 337 | 957 | 1462 | 53 | 1572 | 458 | 62 |
| N.Ireland | 66 | 267 | 586 | 93 | 209 | 139 | 1033 | 143 | 355 | 187 | 334 | 674 | 1494 | 47 | 1506 | 135 | 41 |
# create a heatmap with seaborn
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
sns.heatmap(df_t, cmap='RdYlGn_r', linewidths=0.5, annot=False)
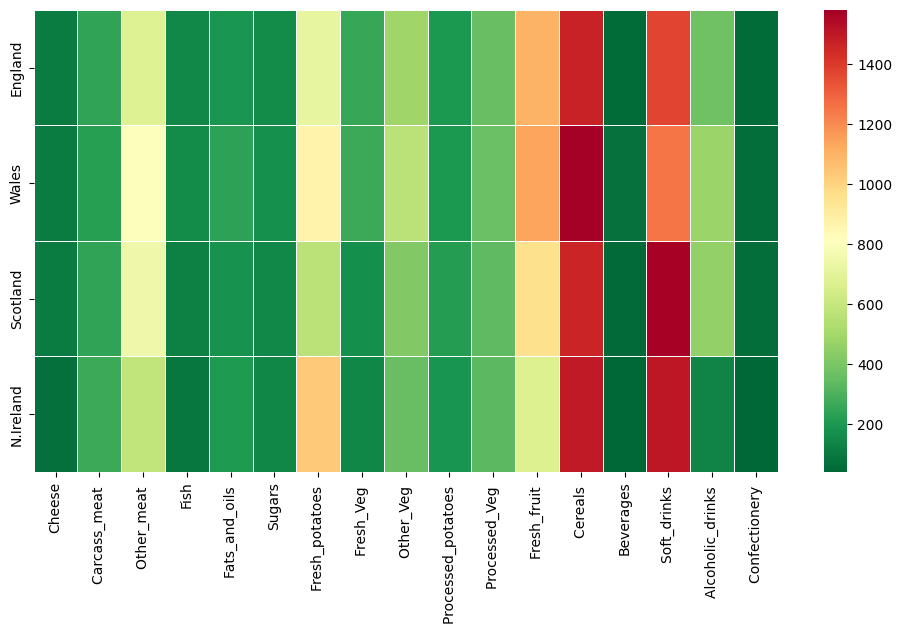
Use an Autoencoder to separate Features
# build the autoencoder
encoder = Sequential([
Dense(units=8, activation='relu', input_shape=[17]),
Dense(units=4, activation='relu'),
Dense(units=2, activation='relu')
])
decoder = Sequential([
Dense(units=4, activation='relu', input_shape=[2]),
Dense(units=8, activation='relu'),
Dense(units=17, activation='relu')
])
autoencoder= Sequential([encoder, decoder])
autoencoder.compile(loss='mse', optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=1e-3))
# normalize input data
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
scaled_df = scaler.fit_transform(df_t.values)
scaled_df.shape
# (4, 17)
autoencoder.fit(scaled_df, scaled_df, epochs=25)
# Epoch 25/25
# 1/1 [==============================] - 0s 5ms/step - loss: 0.2891
# get reduced dimensionality output from encoder
encoded_2dim = encoder.predict(scaled_df)
encoded_2dim
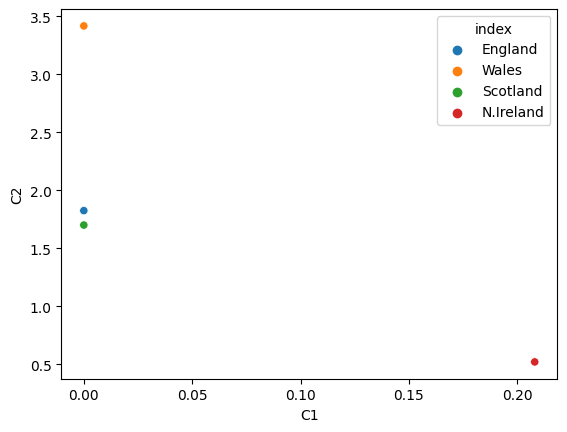
# array([[0. , 1.8262266 ],
# [0. , 3.4182868 ],
# [0. , 1.7019984 ],
# [0.20801371, 0.52220476]], dtype=float32)
results = pd.DataFrame(data=encoded_2dim,
index=df_t.index,
columns=['C1', 'C2'])
results.reset_index()
| index | C1 | C2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | England | 0.000000 | 1.826227 |
| 1 | Wales | 0.000000 | 3.418287 |
| 2 | Scotland | 0.000000 | 1.701998 |
| 3 | N.Ireland | 0.208014 | 0.522205 |
sns.scatterplot(x='C1', y='C2', data=results.reset_index(), hue='index')
# England and Scotland are very close to each other
# while Wales and N.Ireland