Yolo App - YOLOv5 Data Preparation

- Prepare your Images and get Data
- Train your Tensorflow Model
- Use your Model to do Predictions
- Use Tesseract to Read Number Plates
- Flask Web Application
- Yolo v5 - Data Prep
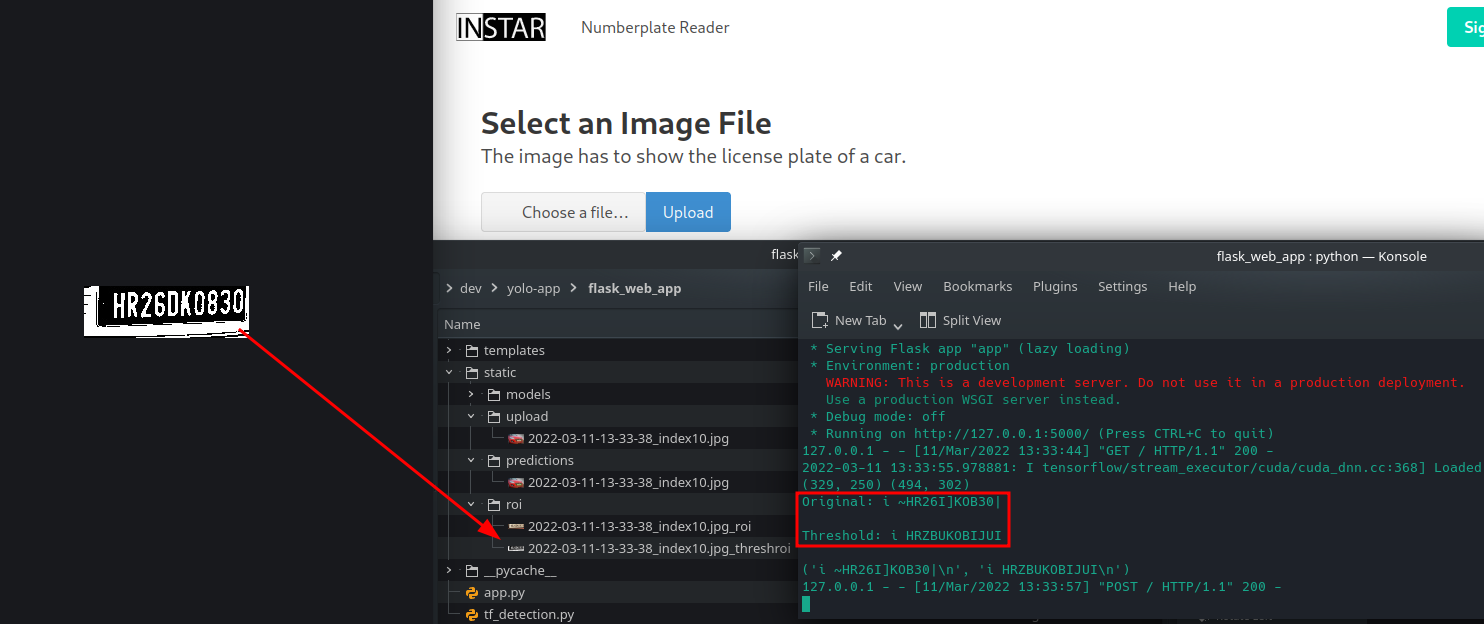
I now have a clean dataset, a working model and a web application for testing. But the detection process is relatively slow and not suitable for real-time video detection. This is where YOLOv5 comes in.
Data Preparation
There is only one problem with the data that was used to train the Tensorflow model. There I needed to define the bounding box around detect license plates byt the variables xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax. But YOLO expects an X & Y value for the center point of the region of interest and it's height & width.
Load Labels
Let's start by importing the labels files for our images:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from glob import glob
import xml.etree.ElementTree as xet
import cv2
import os
import shutil import copy
importdf = pd.read_csv('../labels.csv')
df.head()
filepath xmin xmax ymin ymax
0 ../resources/cars_170.xml 224 439 77 167
1 ../resources/cars_171.xml 416 620 536 600
2 ../resources/cars_172.xml 184 325 114 148
3 ../resources/cars_173.xml 154 373 91 149
4 ../resources/cars_174.xml 131 279 213 256
Parse XML Data
I now need to convert these bbox values to center_x, center_y, width and height and normalize them to their image size. I can start by extracting the image width and height from the generated XML label:
<annotation>
<folder>resources</folder>
<filename>cars_1.jpg</filename>
<path>/opt/yolo-app/resources/cars_1.jpg</path>
<source>
<database>Unknown</database>
</source>
<size>
<width>1600</width>
<height>1153</height>
<depth>3</depth>
</size>
<segmented>0</segmented>
<object>
<name>number_plate</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>1085</xmin>
<ymin>561</ymin>
<xmax>1354</xmax>
<ymax>683</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
</annotation>
The function to parse the image label is:
# Parsing XML labels
def xmlparsing(path):
parser = xet.parse(path).getroot()
image_path = '../' + parser.find('folder').text + '/' + parser.find('filename').text
image_size = parser.find('size')
width = int(image_size.find('width').text)
height = int(image_size.find('height').text)
return image_path, width, height
Now I can append the image width and height to my Pandas dataframe with:
# Take filepath from df and function to append
# image_path, width and height from XML label
df[['image_path','width','height']] = df['filepath'].apply(xmlparsing).apply(pd.Series)
df.head()
filepath xmin xmax ymin ymax image_path width height
0 ../resources/cars_170.xml 224 439 77 167 ../resources/cars_170.jpeg 500 234
1 ../resources/cars_171.xml 416 620 536 600 ../resources/cars_171.jpeg 1070 907
2 ../resources/cars_172.xml 184 325 114 148 ../resources/cars_172.jpeg 500 333
3 ../resources/cars_173.xml 154 373 91 149 ../resources/cars_173.jpeg 500 250
4 ../resources/cars_174.xml 131 279 213 256 ../resources/cars_174.jpeg 414 432
Calculate Bounding Box
And now to getting the variables that are needed by Yolo:
# Calculate center_x, center_y, width and height of bounding box
# and normalize them to image size
df['center_x'] = (df['xmax'] + df['xmin'])/(2*df['width'])
df['center_y'] = (df['ymax'] + df['ymin'])/(2*df['height'])
df['bb_width'] = (df['xmax'] - df['xmin'])/df['width']
df['bb_height'] = (df['ymax'] - df['ymin'])/df['height']
df.head()
filepath image_path width height center_x center_y bb_width bb_height
0 .../cars_170.xml .../cars_170.jpeg 500 234 0.663000 0.521368 0.430000 0.384615
1 .../cars_171.xml .../cars_171.jpeg 1070 907 0.484112 0.626240 0.190654 0.070562
2 .../cars_172.xml .../cars_172.jpeg 500 333 0.509000 0.393393 0.282000 0.102102
3 .../cars_173.xml .../cars_173.jpeg 500 250 0.527000 0.480000 0.438000 0.232000
4 .../cars_174.xml .../cars_174.jpeg 414 432 0.495169 0.542824 0.357488 0.099537
Split Testing and Training Data
Divide image into files used for training and for testing:
# Take first 220 images for training
df_train = df.iloc[:220]
# Take remaining images for testing
df_test = df.iloc[220:]
Create labels for training images and copy everything into the trainings folder:
# Training Data
train_folder = '../data/train'
train_values = df_train[['image_path', 'center_x', 'center_y', 'bb_width', 'bb_height']].values
# Create label and copy images to folder
for fname, x, y, w, h in train_values:
# Get filename from filepath
image_name = os.path.split(fname)[-1]
# Remove file extension
label_name = os.path.splitext(image_name)[0]
# Copy training images to train folder
dst_image_path = os.path.join(train_folder, image_name)
copy(fname,dst_image_path)
# Create image label file
label_values = f'0 {x} {y} {w} {h}'
label_path = os.path.join(train_folder, label_name + '.txt')
with open(label_path , mode='w') as f:
f.write(label_values)
f.close()
And repeat this step for the testing images:
# Testing Data
test_folder = '../data/test'
test_values = df_test[['image_path', 'center_x', 'center_y', 'bb_width', 'bb_height']].values
# Create label and copy images to folder
for fname, x, y, w, h in test_values:
# Get filename from filepath
image_name = os.path.split(fname)[-1]
# Remove file extension
label_name = os.path.splitext(image_name)[0]
# Copy training images to train folder
dst_image_path = os.path.join(test_folder, image_name)
copy(fname,dst_image_path)
# Create image label file
label_values = f'0 {x} {y} {w} {h}'
label_path = os.path.join(test_folder, label_name + '.txt')
with open(label_path , mode='w') as f:
f.write(label_values)
f.close()