Yolo App - Pipeline Predictions

- Prepare your Images and get Data
- Train your Tensorflow Model
- Use your Model to do Predictions
- Use Tesseract to Read Number Plates
- Flask Web Application
- Yolo v5 - Data Prep
Model Predictions
Loading the Model
I can now load the trained model and try to run a prediction:
import numpy as np
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import load_img, img_to_array
# Load the trained model
model = tf.keras.models.load_model('../models/object_detection.h5')
print('[INFO] object detection model loaded')
Memory Error in Tensorflow:
I tensorflow/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_gpu_executor.cc:936] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero
Running the following command from my console to set each device to 0 got rid of the warning:
for a in /sys/bus/pci/devices/*; do echo 0 | sudo tee -a $a/numa_node; done
Load a Test Image
I now need to pick an image the model was not trained on to check to models accuracy:
# Pick a test image that your model was not trained on
path = './test_images/index5.jpg'
image = load_img(path) # PIL object
# convert into array and get the normalized output
image = np.array(image,dtype=np.uint8) # 8 bit array (0,255)
image1 = load_img(path,target_size=(224,224))
image_arr_224 = img_to_array(image1)/255.0
# Get size of the orginal image
h,w,d = image.shape
print('Image height:',h)
print('Image width:',w)
# Show selected image
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8))
plt.imshow(image)
plt.show()
Predict Number Plate Coordinates
# Check if dimensions are OK
image_arr_224.shape
# Add index number colume to shape
test_arr = image_arr_224.reshape(1,224,224,3)
test_arr.shape
# Use trained model to predict
# number plate location
coords = model.predict(test_arr)
coords
# Denormalize output
denorm = np.array([w,w,h,h])
coords = (coords * denorm).astype(np.int32)
coords
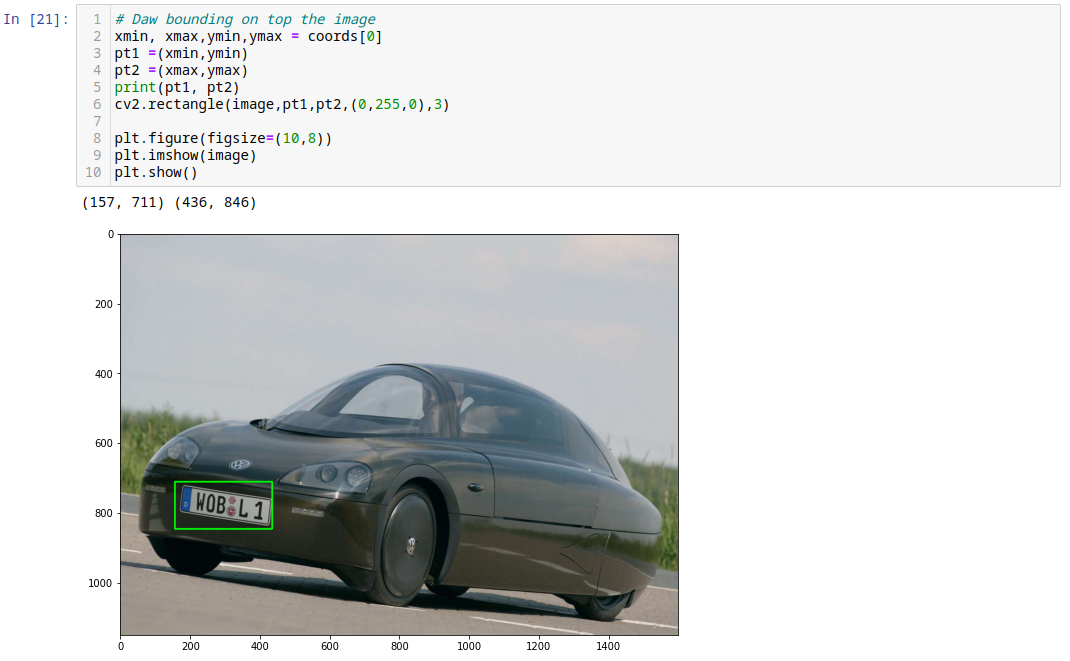
# Daw bounding on top the image
xmin, xmax,ymin,ymax = coords[0]
pt1 =(xmin,ymin)
pt2 =(xmax,ymax)
print(pt1, pt2)
cv2.rectangle(image,pt1,pt2,(0,255,0),3)
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8))
plt.imshow(image)
plt.show()
Detection Pipeline
I can now wrap everything into a single function:
# Wrap all steps into a function
def object_detection(path):
# Read image
image = load_img(path) # PIL object
image = np.array(image,dtype=np.uint8) # 8 bit array (0,255)
image1 = load_img(path,target_size=(224,224))
# Data preprocessing
image_arr_224 = img_to_array(image1)/255.0 # convert into array and get the normalized output
h,w,d = image.shape
test_arr = image_arr_224.reshape(1,224,224,3)
# Make predictions
coords = model.predict(test_arr)
# Denormalize the values
denorm = np.array([w,w,h,h])
coords = coords * denorm
coords = coords.astype(np.int32)
# Draw bounding on top the image
xmin, xmax,ymin,ymax = coords[0]
pt1 =(xmin,ymin)
pt2 =(xmax,ymax)
print(pt1, pt2)
cv2.rectangle(image,pt1,pt2,(0,255,0),3)
return image, coords
I can test the function on another image:
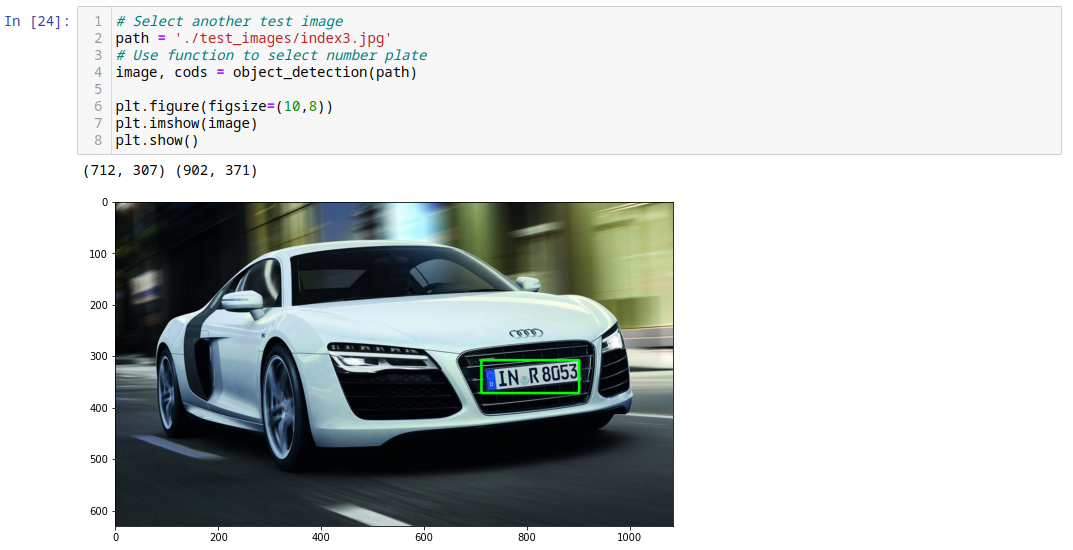
# Select another test image
path = './test_images/index3.jpg'
# Use function to select number plate
image, cods = object_detection(path)
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8))
plt.imshow(image)
plt.show()